Figure 3. CXCR5+CD8+ T cells from CCR5 KO (compared to WT) kidney transplant recipients mediate impaired in vitro and in vivo cytotoxicity to alloprimed B cell targets.
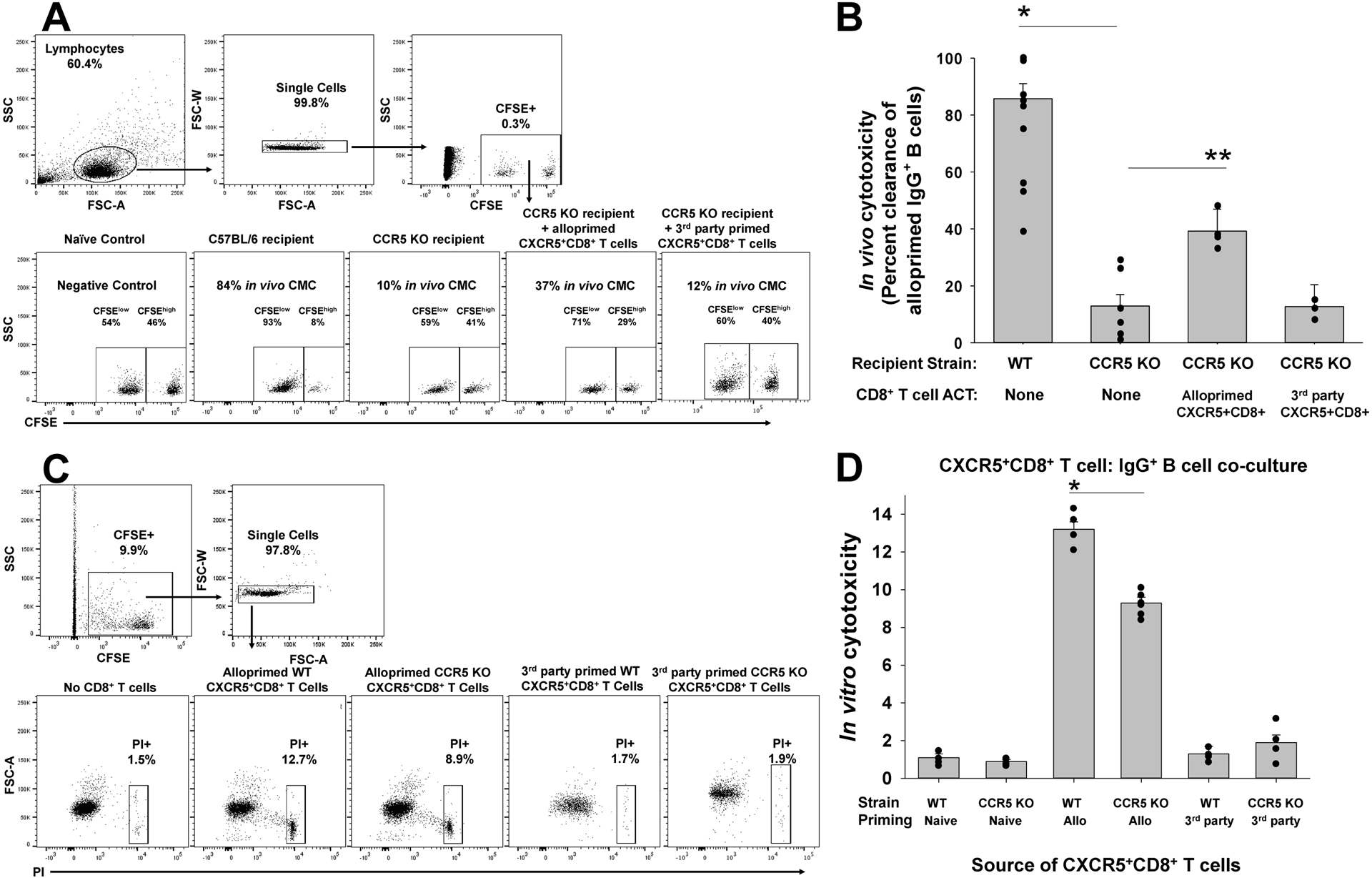
A) C57BL/6 (WT) and CCR5 KO mice (both H-2b) were transplanted with A/J (H-2a) kidney. On day 7, CFSEhi-labeled alloprimed IgG+ B cells were adoptively transferred (along with control, CFSElo naïve B220+ B cells) into transplant recipients to test for in vivo cytotoxic clearance of IgG+ B cells. A) Representative flow plots show gating on lymphocytes, single cells, and CFSElo naïve B cells and CFSEhi alloprimed IgG+ B cells that were used to determine vivo cytotoxicity. B) In vivo cytotoxicity to IgG+ B cells was significantly reduced in CCR5 KO recipients compared to WT recipients (12.9±4.0% vs. 85.7±5.3%, n=7 and n=10, respectively; *p<0.0001). Adoptive cell therapy (ACT) with alloprimed CXCR5+CD8+ T cells from WT mice significantly increased in vivo cytotoxicity to alloprimed B cell targets in CCR5 KO recipients (39.2±7.7%; n=4; **p=0.0004) compared to untreated CCR5 KO recipients. ACT with third party-primed CXCR5+CD8+ T cells was not associated with an increase in in vivo cytotoxicity to alloprimed IgG+ B cells (12.7±7.7%, n=4; p=ns) compared to CCR5 KO recipients without ACT. C) Next, we performed in vitro cytotoxicity using CXCR5+CD8+ T cells and alloprimed CFSE-labeled B cells in co-cultures. Propidium iodide (PI) was used to assess viability of B cells after 4 hours in co-culture. Representative flow plots show gating on CFSE+IgG+ B cell targets, single cells, and propidium iodide (PI). D) WT and CCR5 KO mice were alloprimed with A/J kidney lysate (2mg). On day 7, CXCR5+CD8+ T cells retrieved from the spleen were flow-sorted for in vitro cytotoxicity assays. Alloprimed CXCR5+CD8+ T cells from CCR5 KO mice mediated significantly less in vitro cytotoxicity to IgG+ B cells compared to those from WT mice (9.3±0.3 vs.13.2±0.4%, both groups n=6; *p=0.0001). Third-party primed WT or CCR5 KO CXCR5+CD8+ T cells did not mediate significant cytotoxicity to IgG+ B cells in vitro (1.3±0.4% and 1.9±0.4%, respectively; n=4 and p=ns for both).
