Figure 5. Adoptive cell therapy with alloprimed CXCR5+CD8+ T cells into CCR5 KO kidney transplant recipients significantly reduces the proportion of splenic germinal center B cells.
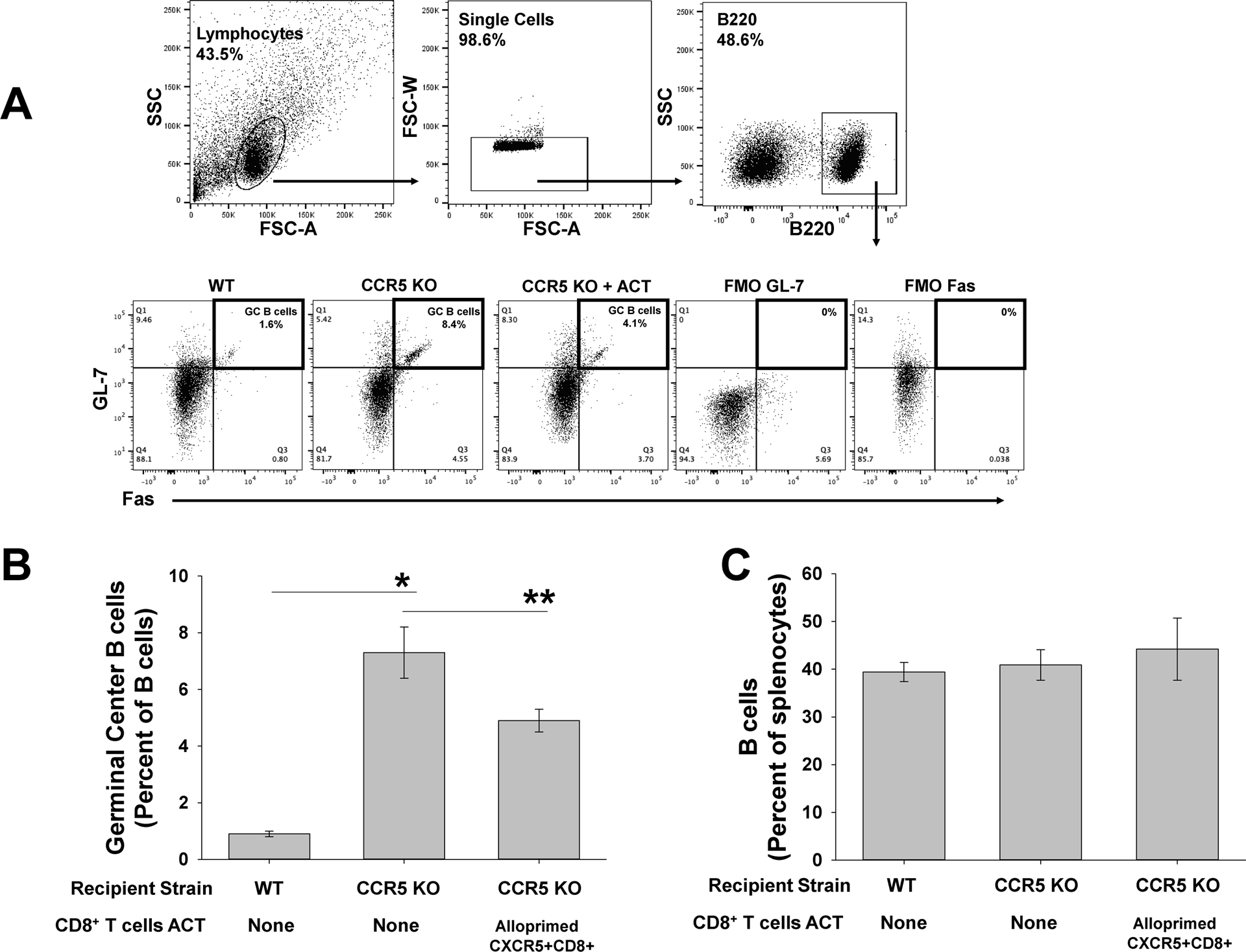
C57BL/6 (WT) and CCR5 KO mice (both H-2b) were transplanted with A/J (H-2a) kidney. On posttransplant day 5, a cohort of CCR5 KO recipients underwent ACT with 2×106 CXCR5+CD8+ T cells. Splenocytes were retrieved for analysis of germinal center (GC) B cells (B220+Fas+GL-7+) on day 14 posttransplant. A) Representative flow cytometric gating on lymphocytes, single cells, and B220+ cells are shown. Fluorescent minus one was used as a negative control. B) The proportion of GC B cells (GL-7+Fas+B220+) was significantly higher in CCR5 KO recipients (7.3±0.9%, n=5) compared to WT recipients (0.9±0.1%, n=5; *p<0.0001). Following ACT with 2.0×106 alloprimed CXCR5+CD8+ T cells, the proportion of splenic GC B cells was significantly reduced in CCR5 KO recipients (4.9±0.4%, n=6; **p=0.002). C) No significant difference in overall quantity of splenic B cells was observed between WT and CCR5 KO recipients (p=ns).
