Figure 6. Adoptive cell therapy with alloprimed CXCR5+CD8+ T cells into CCR5 KO kidney transplant recipients ameliorate antibody-mediated rejection pathology.
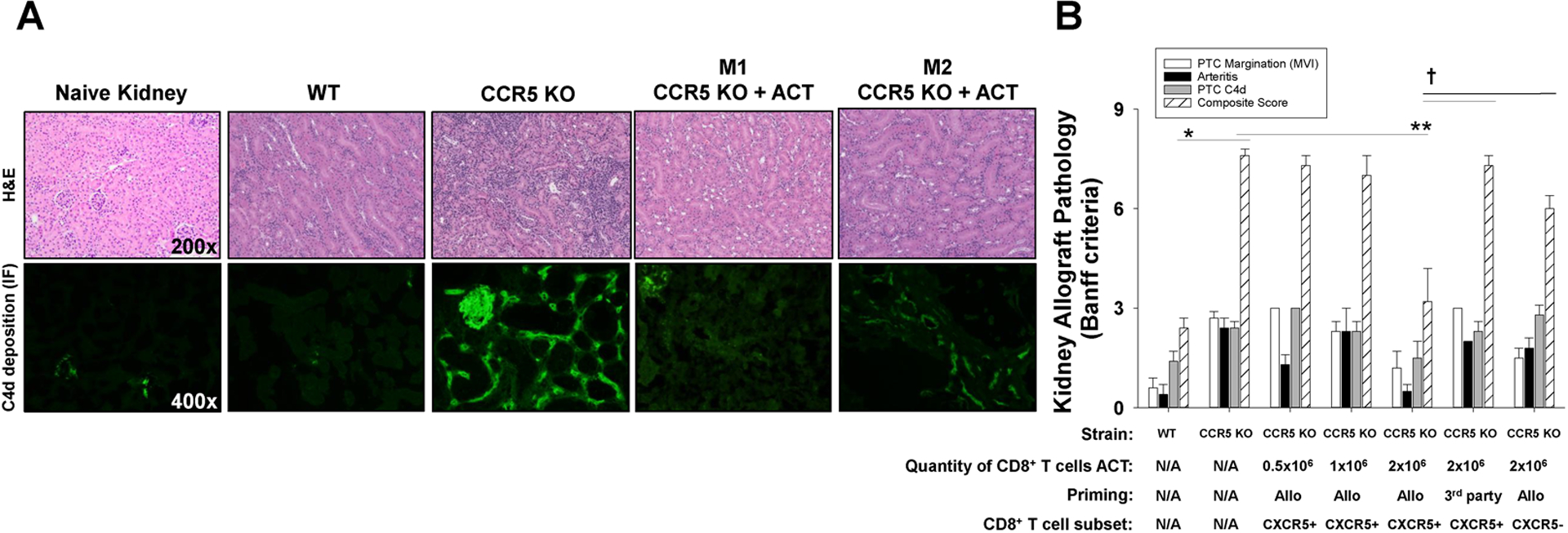
C57BL/6 and CCR5 KO (both H-2b) mice were transplanted with allogeneic (A/J, H-2a) kidneys. A cohort of CCR5 KO recipients received adoptive cell therapy (ACT) with alloprimed CXCR5+CD8+ T cells (0.5×106 to 2×106 cells; day 5 posttransplant) or 3rd party (FVB/N, H-2q) primed CXCR5+CD8+ T cells (2×106). On day 14 posttransplant, allografts were removed for histological analysis. A) Histology and C4d immunofluorescence of tissue samples from each group were analyzed (representative data shown). Kidney pathology in CCR5 KO recipients that received ACT had significantly less inflammation and C4d deposition compared to CCR5 KO recipients without ACT. There was some variability in the amount of inflammation in CCR5 KO mice that received ACT ranging from minimal PTC inflammation (or C4d deposition) observed in mouse 1 (M1: CCR5 KO + ACT) to reduced inflammation and C4d deposition as observed in mouse 2 (M2: CCR5 KO + ACT). B) Samples were scored according to Banff criteria. The individual histologic scores for PTC margination, arteritis, and PTC C4d deposition, as well as histologic composite score are shown for experimental groups. Composite AMR score in CCR5 KO recipients (7.6±0.4, n=7) was significantly higher than in C57BL/6 recipients (2.4±0.5, n=5; *p<0.0001). Composite AMR scores in CCR5 KO recipients that received ACT with 2.0×106 alloprimed CXCR5+CD8+ T cells (3.2±2.6, n=6) were significantly lower than in CCR5 KO recipients without ACT (7.6±0.4, n=7; **p<0.0001) indicating substantial amelioration of AMR pathology. In contrast, composite AMR scores in CCR5 KO recipients transferred with 0.5×106 (7.3±0.6, n=3) or 1.0×106 (7.0±1.0, n=3) alloprimed CXCR5+CD8+ T cells, 2.0×106 3rd party primed CXCR5+CD8+ T cells (7.25±0.5, n=4), or 2.0×106 alloprimed CXCR5−CD8+ T cells (6.0±0.4, n=4) were similar to AMR score in CCR5 KO recipients without ACT (p=ns for all comparisons) and significantly greater than AMR score in CCR5 KO recipients after ACT with 2.0×106 alloprimed CXCR5+CD8+ T cells (p<0.002 for all comparisons).
