Figure 1. Structure of the KIT receptor.
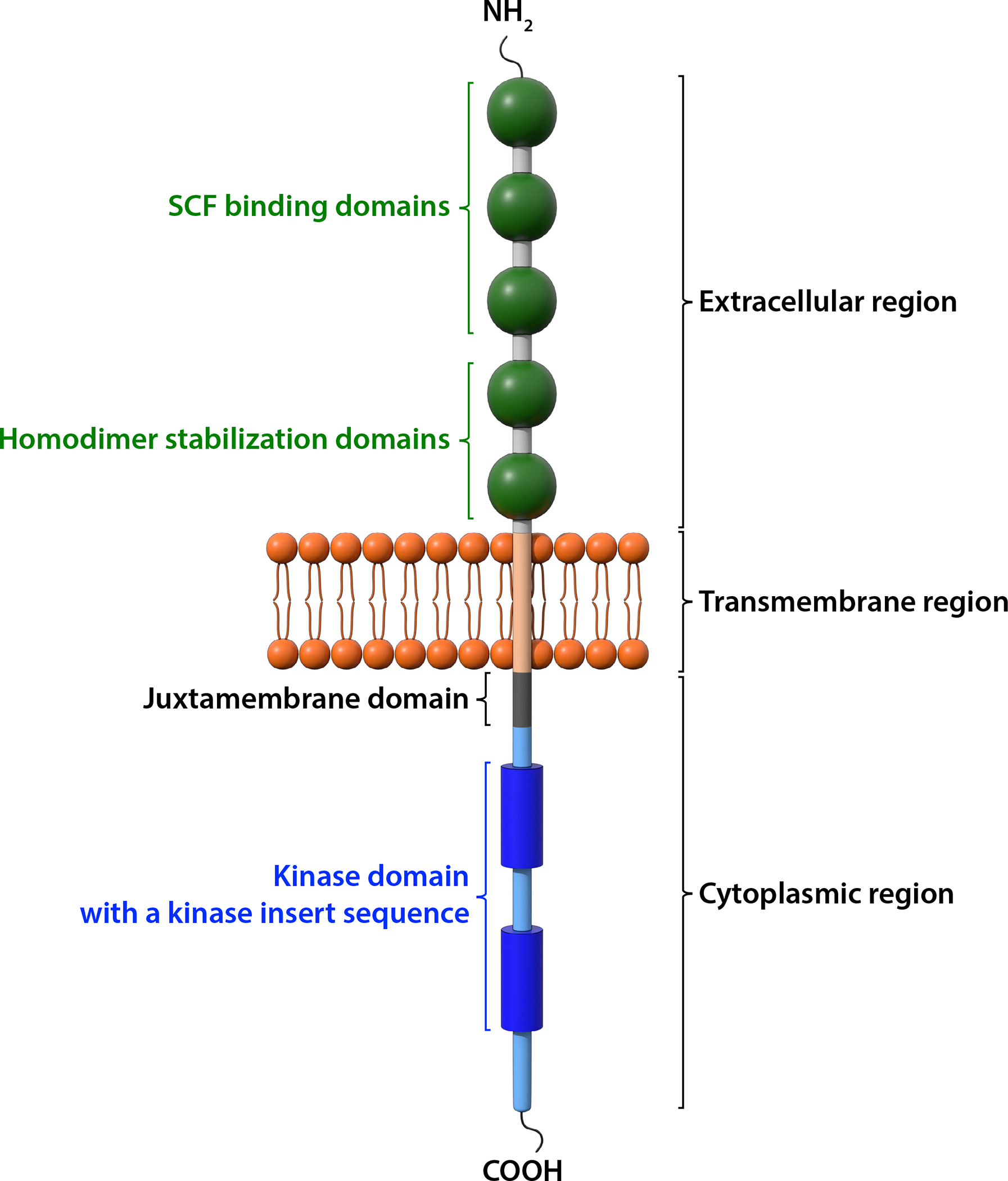
KIT is a member of the receptor tyrosine kinase III family. It consists of an extracellular region, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic region. There are five immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains in the extracellular region. The first three Ig-like domains bind to SCF and the 4th and 5th Ig-like domains facilitate dimerization upon ligand binding. The intracellular tyrosine kinase domain is interrupted by a hydrophilic insert sequence. The juxtamembrane domain, the kinase domain and the carboxyl terminal tail are involved in signal transduction when the KIT receptor is activated.
