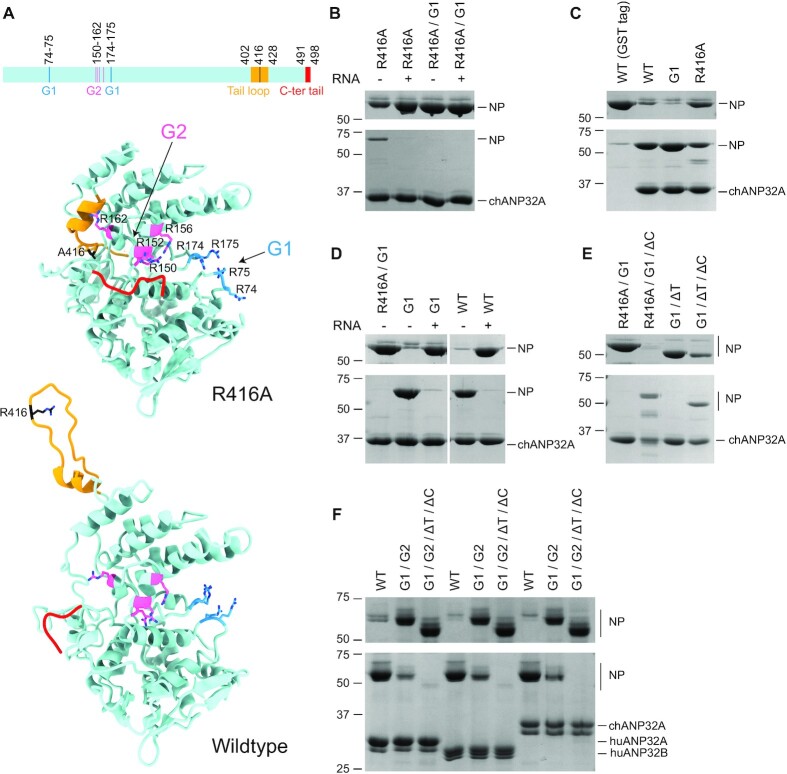
Figure 3.
RNA binding grooves of NP are involved in the interaction with ANP32 proteins. (A) Schematic diagram and structural models of influenza A virus NP (R416A, PDB ID: 3ZDP, and wildtype, PDB ID: 2Q06) showing the G1 (blue) and G2 (pink) RNA binding grooves, tail loop (yellow), and C-terminal tail (red). Key amino acid residues in both the RNA binding grooves and tail loop are shown in stick mode in structural models. (B–F) GST pull-down assays using GST tagged chANP32A, huANP32A or huANP32B and wildtype or mutant NP in the absence or presence of 1.5× (+) molar excess of a 29-nt RNA (B, D). The following NP mutants were used: R416A, G1 (R74A/R75A/R174A/R175A), G2 (R150A/R152A/R156A/R162A), ΔT (amino acid residues 402–428 of the tail loop deleted), ΔC (amino acid residues 491–498 of the C-terminal tail deleted), and their combinations. ANP32 proteins with a cleavable N-terminal GST tag were immobilized on glutathione sepharose before the addition of wildtype or mutant NP. Bound proteins were released by treatment with PreScission protease. A purified GST tag alone was used as negative control (C). Unbound (upper gels) and released (lower gels) samples were analysed by SDS-PAGE and staining with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. Molecular weight markers are indicated in kDa.