Figure 7.
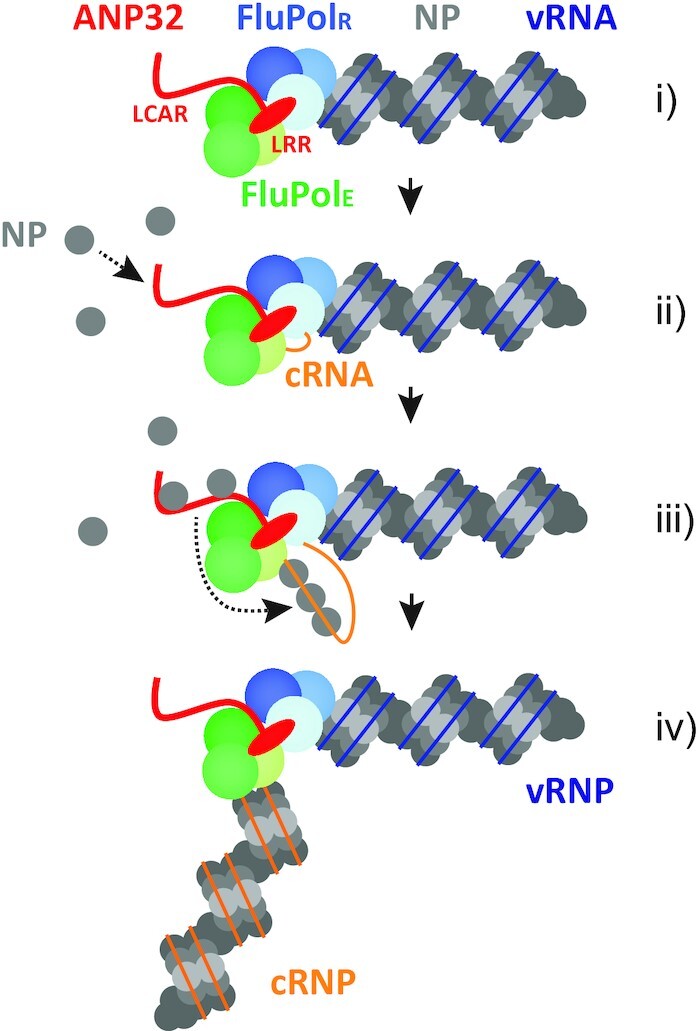
Model of influenza virus RNA genome replication. (i) ANP32 mediates the recruitment of a free influenza virus polymerase (encapsidating polymerase, FluPolE) to the polymerase resident in a vRNP (replicating polymerase, FluPolR) through its N-terminal LRR domain (red oval), leading to polymerase dimerization. (ii) FluPolR initiates cRNA synthesis and the 5′ end of the nascent cRNA (orange) is captured by FluPolE. The flexible C-terminal LCAR of ANP32 (red line) recruits free NP molecules and increases local NP density. (iii) ANP32 LCAR facilitates the transfer of NP to nascent cRNA. NP dissociates from the LCAR and binds to cRNA due to its higher affinity to RNA. (iv) cRNA is assembled into a mature cRNP before being released from the template vRNP complex.
