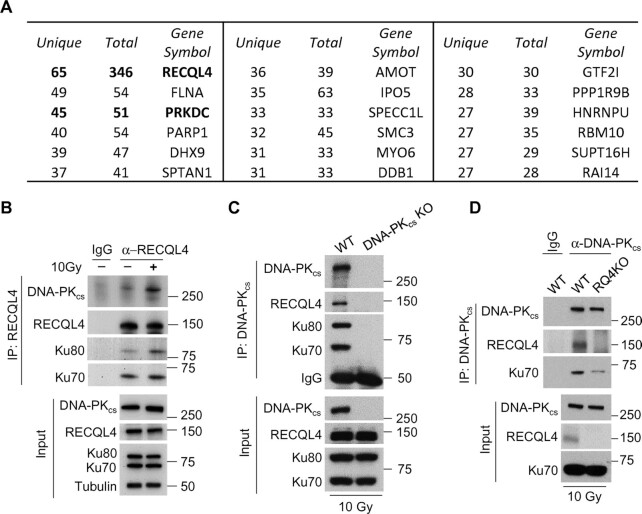
Figure 1.
Ionizing radiation stimulates the interaction between RECQL4 and DNA-PKcs. (A) Identification of RECQL4-associated proteins following DNA damage. U2OS cells were irradiated with 10 Gy of IR, allowed to recover for 10 min, and RECQL4 was immunoprecipiated from whole cell lysates. The samples were resolved via SDS-PAGE, stained, and then analyzed using mass spectrometry analysis. Shown are the top 17 RECQL4-interacting proteins identified in the screen. DNA-PKcs (gene: PRKDC) was a top hit in the RECQL4 protein-protein interaction screen. (B) DNA damage promotes the interaction between RECQL4 and the DNA-PK complex (Ku70/80 heterodimer and DNA-PKcs). U2OS cells were mock treated or irradiated with 10 Gy and allowed to recover for 10 min. Endogenous RECQL4 was immunoprecipitated and its interaction with the DNA-PK complex was assessed via immunoblotting using DNA-PKcs, Ku70 and Ku80 antibodies. (C) DNA-PKcs was immunoprecipitated from HCT116 wild-type (WT) or DNA-PKcs knockout (DNA-PKcs KO) cells that were treated with 10 Gy of IR and allowed to recover for 10 min. The samples were resolved via SDS-PAGE and the interaction between DNA-PKcs and RECQL4 and Ku70/80 was determined via immunoblotting. (D) DNA-PKcs was immunoprecipitated from U2OS wild-type (WT) or RECQL4 knockout (RQ4KO) cells that were irradiated with 10 Gy of IR and allowed to recover for 10 min. The samples were resolved via SDS-PAGE and interaction between RECQL4 and DNA-PKcs and Ku70/80 was determined via immunoblotting.