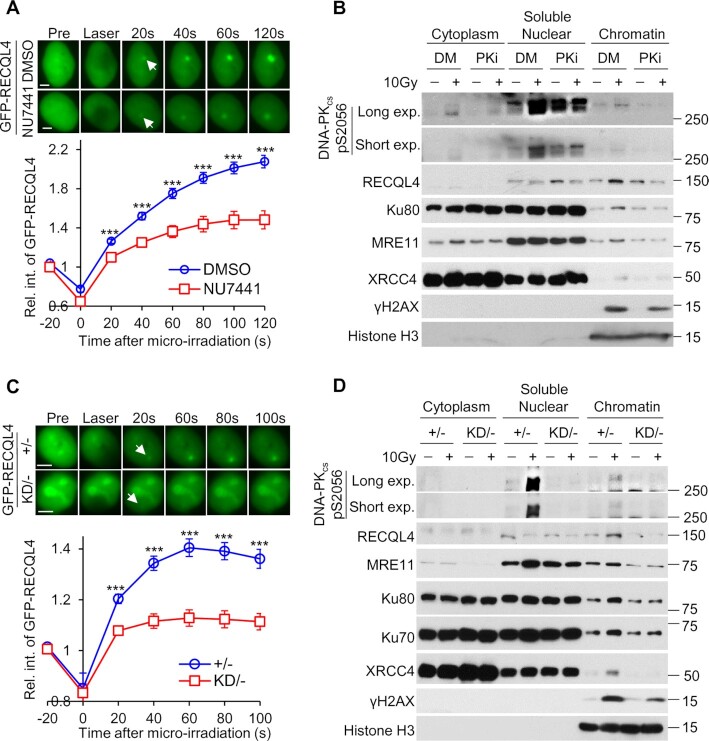
Figure 4.
The kinase activity of DNA-PKcs promotes the accumulation of RECQL4 at DSBs. (A) Inhibition of DNA-PKcs attenuates accumulation of RECQL4 at laser-induced DSBs. U2OS RECQL4 Knockout cells stably expressing GFP-tagged RECQL4 were pretreated either with DMSO or 10 μM NU7441 for 2 h, and subsequently laser micro-irradiation assays were performed. Relative fluorescent intensity of GFP-tagged RECQL4 following micro-irradiation are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Samples analyzed were 15 for DMSO-treated and 16 NU7441-treated cells. Student's t-test (two-sided) was performed to assess statistical significance (*** P< 0.001). (B) Inhibition of DNA-PKcs reduces the recruitment of RECQL4 to the chromatin fraction following IR. U2OS cells were pretreated with 10 μM NU7441 or DMSO for 2 h, mock-treated or irradiated with a dose of 10 Gy, and allowed to recover for 10 min. Subsequently, cytoplasmic, soluble nuclear and chromatin fractions were isolated for immunoblotting to examine the recruitment of proteins listed in the figure to the chromatin after irradiation. (C) Accumulation of GFP-tagged RECQL4 in HCT116 DNA-PKcs kinase-dead (KD/–) cells is reduced compared to that in control DNA-PKcs+/– cells (+/–). Relative fluorescent intensity of GFP-tagged RECQL4 following micro-irradiation are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Samples analyzed were 8 for +/– and 8 for KD/– cells. Student's t-test (two-sided) was performed to assess statistical significance (*** P< 0.001). (D) Recruitment of RECQL4 to the chromatin fraction is decreased in KD/– cells compared to +/– cells. KD/– and +/– cells were mock-treated or irradiated with a dose of 10 Gy and allowed to recover for 10 minutes. Subsequently, cytoplasmic, soluble nuclear and chromatin fractions were isolated for immunoblotting to examine the recruitment of proteins listed in the figure to the chromatin after irradiation.