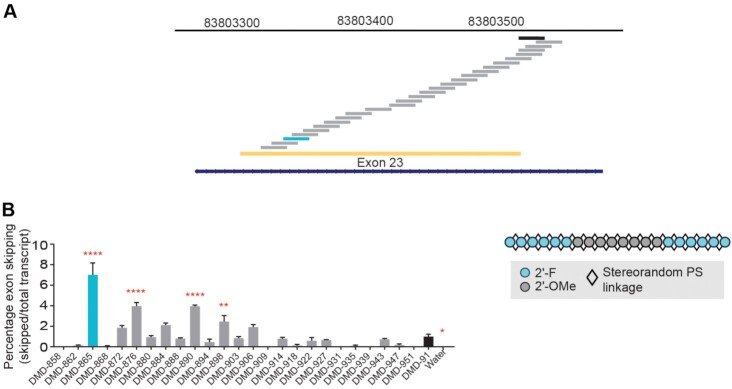
Figure 3.
Identification of exon 23 skipping site. (A) To identify an exon 23 skipping targeting sequence, we screened oligonucleotides (depicted by staggered bars) complementary to sequences in and around exon 23 (yellow) of the mouse Dmd gene (cytogenetic view at top) using oligonucleotides with the chemistry mask identified from preliminary studies (shown in panel B). (B) Exon 23 skipping percentages in H2K cells treated gymnotically with 10 μM of the indicated oligonucleotides (shown in Supplementary Table S1) that differ in sequence but have the same chemical modifications (illustrated to the right). Analysis revealed a new targeting sequence (light blue) that is suitable for mediating efficient exon-23 skipping. DMD-91 (black) targets a previously published comparator sequence (5′- GGCCAAACCUCGGCUUACCU -3′) (26). ****P < 0.0001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05 One-way ANOVA with post-hoc comparisons to DMD-91. Mean ± s.e.m., n ≥ 3.