Fig. 2. Basophil responses in the skin.
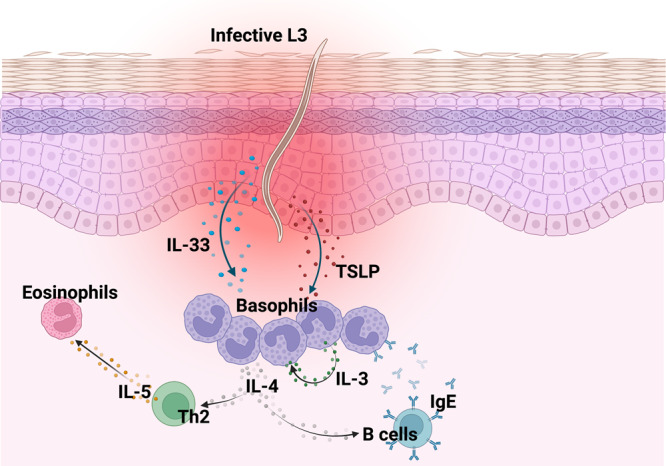
Infective L3 penetrate the skin causing damage of the epithelial cells. Alarmins such as IL-33 and TSLP are released from damaged epithelial cells. Both IL-33 and TSLP can activate basophils, which can release IL-4. IL-4 is necessary for 1) the development of TH2 cells and the release of IL-5 involved in eosinophil recruitment, and 2) B cell IgE class switching. Basophil activity is directed against the parasite upon binding of IgE through high affinity receptors and trapping infective larvae. TSLP together with IL-3 induces recruitment of basophils at the site of skin inflammation.
