Fig. 3. Immune responses against invading parasite in the lung.
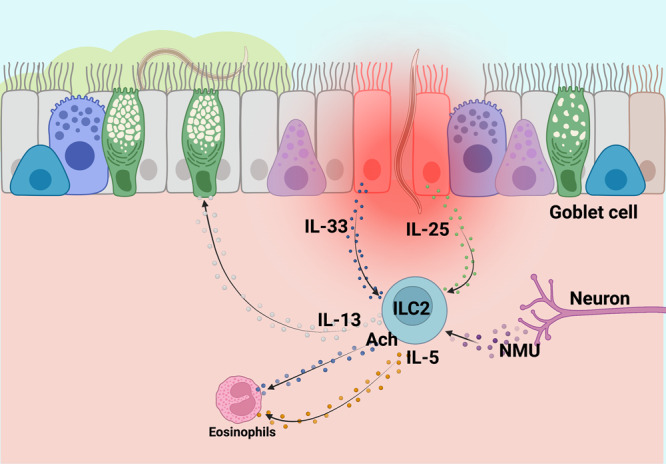
Hookworm larvae can cause extensive damage during the lung migratory phase. The release of IL-33 and IL-25, from damaged epithelial cells, and NMU from neurons drives the activation of ILC2s. Activated ILC2s release IL-5 and ACh, involved in eosinophils recruitment, and IL-13 that acts on goblet cells and increases mucus production. Both the presence of activated eosinophils and increased mucus production help with the killing and removal of parasites.
