Figure 4.
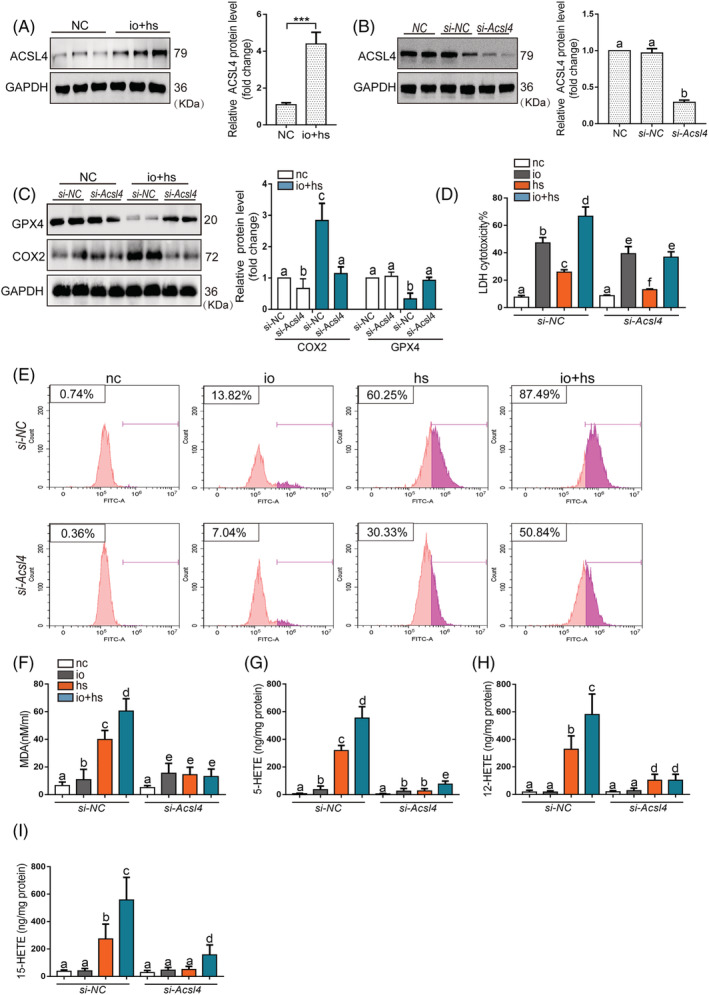
The effects of genetic inhibition of Acsl4 on the viability and lipid peroxidation of primary myoblasts cells exposed to io + hs in vitro. (A) Western blotting was used to determine ACSL4 expression of primary myoblasts in the presence or absence of io + hs exposure, the representative images of western blotting were from three independent experiments. (B) Primary myoblast were transfected with si‐NC or si‐Acsl4 for 2 days before io + hs induction. All samples were collected at 6 h after io + hs induction. ACSL4 expression level under io + hs induction for 2 h after siRNA transfection was assessed by western blotting, the representative images of western blotting were from three independent experiments. (C) GPX4 and ACSL4 protein levels were determined by western blotting after io + hs induction, the representative images of western blotting were from three independent experiments. (D) The LDH cytotoxicity percent was assayed at 6 h after io + hs induction (n = 6). (E) Cell lipid peroxidation signal was detected by C11 BODIPI 581/591 staining by flow cytometry. (F–I) In parallel, the levels of MDA, 5‐HETE, and 15‐HETE were assayed at 6 h following io + hs exposure (n = 6). Significance was calculated using the Student's t‐test; *P < 0.05. Summary data are presented as the mean ± SEM. Significance was calculated using a one‐way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test; groups labelled with different letters differed significantly (*P < 0.05).
