Figure 1.
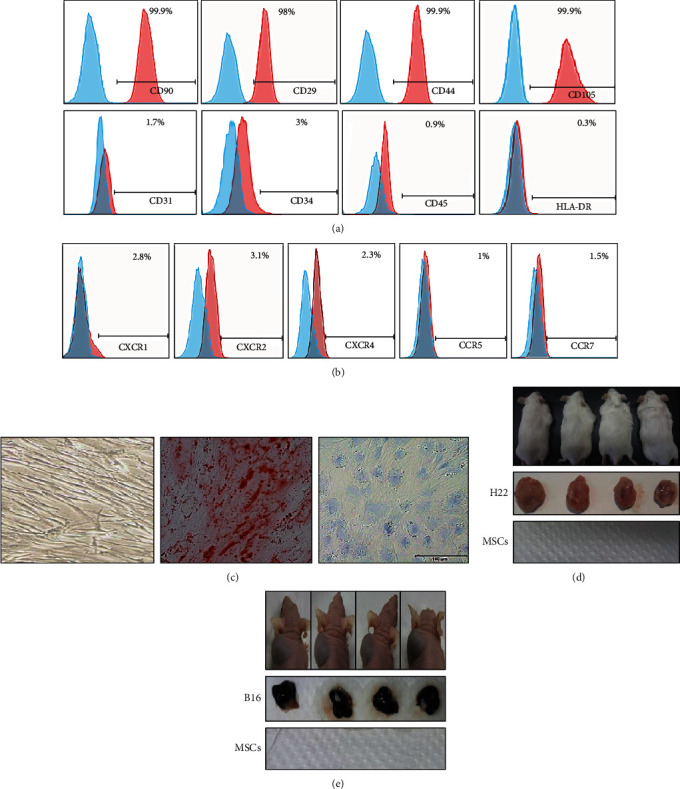
Characterization and the safety evaluation of HUC-MSCs isolated from Wharton jelly of the umbilical cord. (a) Identification of the expression of MSC markers by flow cytometry. CD29, CD44, CD90, and CD105 were highly expressed in HUC-MSCs, while CD31, CD34, CD45, and HLA-DR were lowly expressed. (b) HUC-MSCs express detectable chemokine receptors. (c) Multilineage differentiation potential of HUC-MSCs. HUC-MSC control (left); Oil Red O staining for adipogenic differentiation (middle); Alcian Blue staining for osteogenic differentiation. To make sure of the safety of HUC-MSC injection, tumor-bearing experiment was used in immunodeficiency and normal immunity mice. Error bars: mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.005. (d) The same amount of HUC-MSCs and H22 cells (5 × 106 cells) was, respectively, injected into the left and right side of ICR mice to compare tumor formation ability of HUC-MSCs and H22 cells (n = 6). (e) The same amount of HUC-MSCs and B16 cells (1 × 106 cells) was, respectively, injected into the right and left side of nude mice to compare tumorigenesis ability in vivo (n = 7).
