Figure 3.
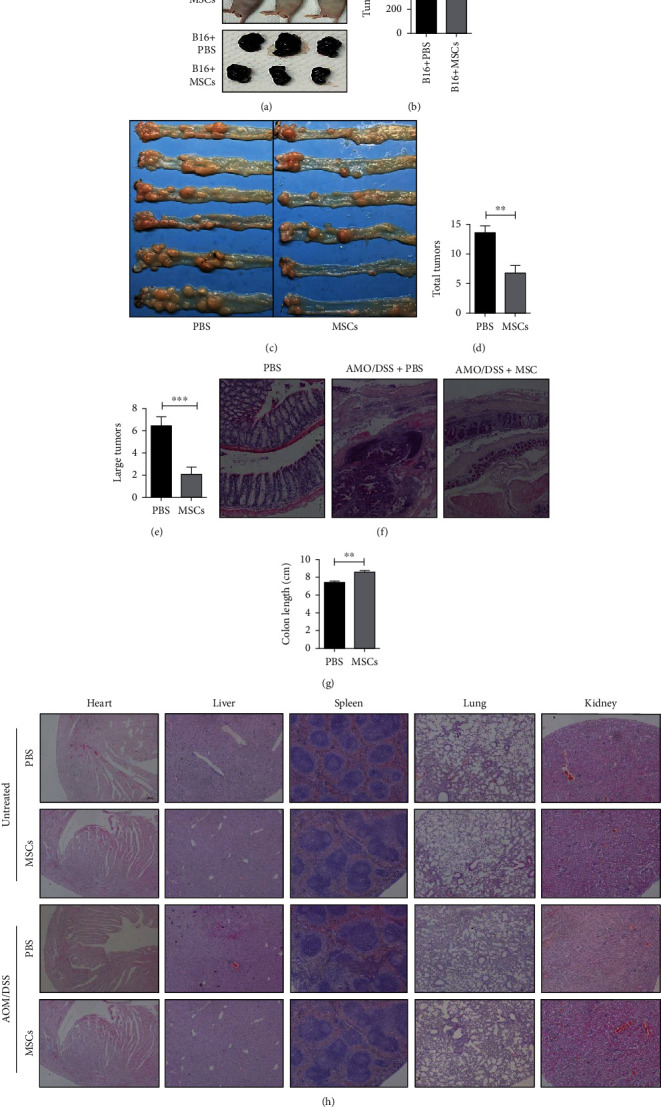
HUC-MSCs effectively inhibit tumorigenesis. (a, b) The same amount of B16 cells (1 × 106 cells) was injected into the left side of PBS and HUC-MSC group nude mice; then, 1 × 106 HUC-MSCs were intravenously injected into the MSC group twice a week, and the same amount of PBS was injected into the PBS group to observe the occurrence of tumors (n = 6). (c) HUC-MSC injection reduces colonic tumor burden in C57BL/6J mice induced by AOM/DSS (n = 5). (d, e) Tumor numbers in the PBS and HUC-MSC group after treatment with AOM/DSS. (f) Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining of colons. Intravenous injection of HUC-MSCs promotes histological improvement. (g) Colon length in the PBS and HUC-MSC group after treatment with AOM/DSS. (h) Pathologic section of the colon, heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney in the PBS and HUC-MSC group treated with AOM/DSS. HUC-MSCs were intravenously injected once a week. No tumors were found in the heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney injected with or without HUC-MSCs.
