Figure 4.
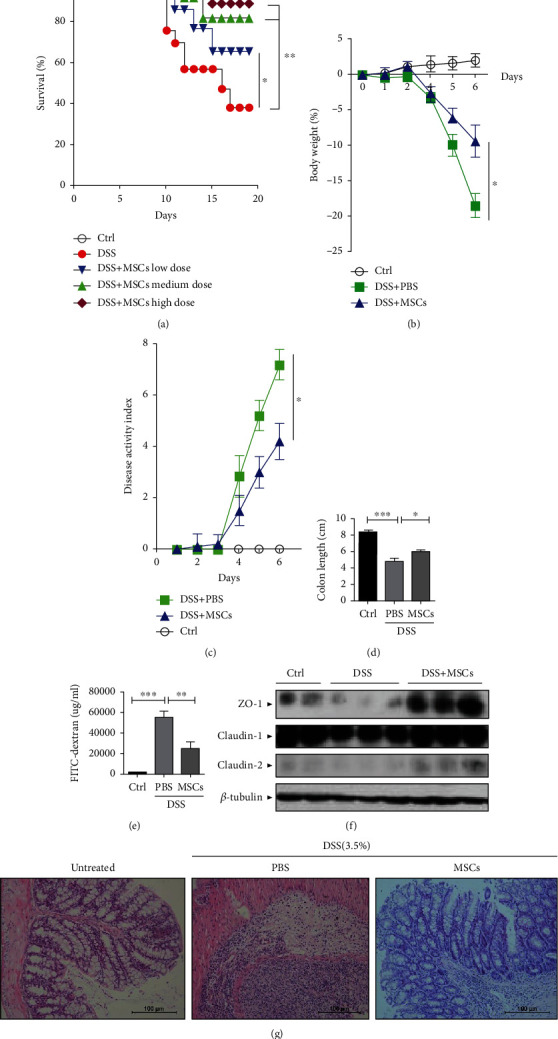
HUC-MSC treatment protects against DSS-induced acute colitis. Colitis was induced by oral administration of 3.5% (wt/vol) DSS in sterile drinking water for 6 days. Mice were injected intravenously with 2 × 106 HUC-MSCs in 200 μl phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) per mouse in the cell injection group or with 200 μl PBS per mouse in the DSS-treated group at day 1, day 3, and day 5. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.005. Error bars: mean ± SD. (a) Survival rate of mice treated with 5% (wt/vol) DSS and different doses of HUC-MSCs. The dose of cells injected into mice was 1 × 105, 2 × 105, and 5 × 105 per mice. (b) Weight changes of mice with or without 3.5% (wt/vol) DSS treatment. (c) Disease activity index (DAI) scores after DSS administration. Clinical evolution was monitored by weight change, stool consistency, and presence of fecal blood. (d) Statistics of colon lengths in normal, DSS-, and HUC-MSC-treated groups. (e) Evaluation of colonic permeability with FITC-dextran in serum of colitis mice. (f) Evaluation of colonic permeability with western blot. (g) Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining of colons. Intravenous injection of HUC-MSCs promotes histological improvement. Colon histology demonstrated intravenously administered HUC-MSCs reduced the extent of the inflamed area, crypt damage, and infiltration of inflammatory cells caused by DSS.
