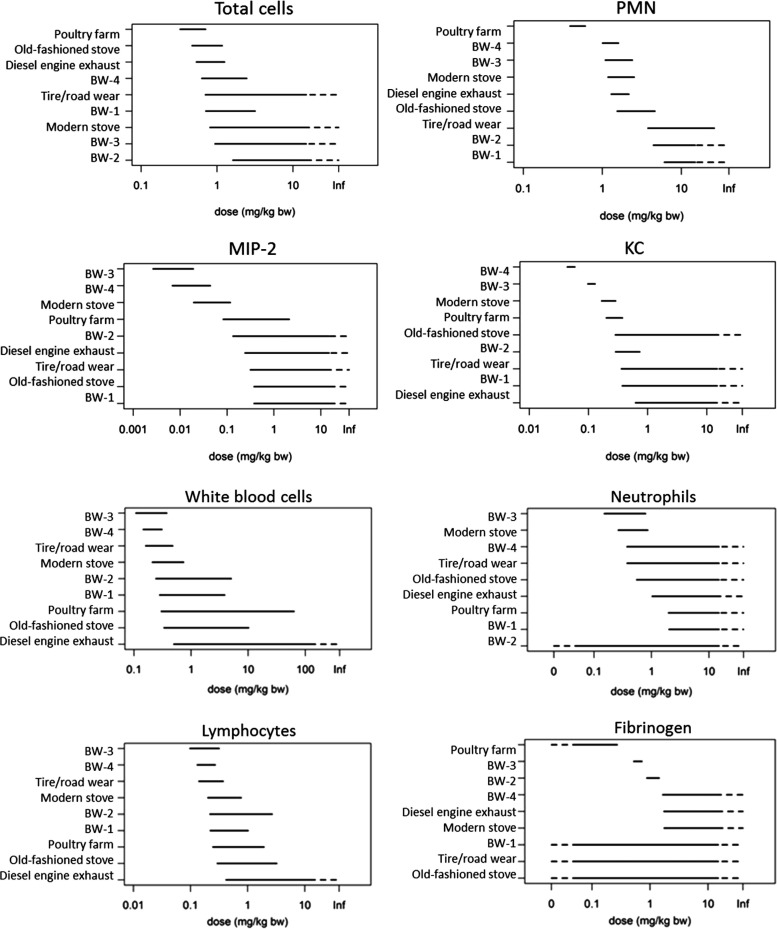
Figure 3.
Relative toxicity of BWP compared to particulates from other sources following inhalation in mice. The further the line is to the left, the lower the dose at which it exerts an effect (i.e., the greater the toxicity) for that given parameter. In several assays, BWP had a greater effect than tire wear, DEP, and other PM. Equally, the relative toxicity varied considerably between the parameter being studied. Upper four panels are measures of pulmonary inflammation, lower four panels are markers of systemic inflammation. BW-1 = BW from low metallic pads but with some copper, BW-2 = BW from semimetallic pads with no copper, BW-3 = BW from organic brake pads, BW-4 = BW from organic and metallic hybrid pads, KC = keratinocyte-derived chemokine, MIP-2 = macrophage inflammatory protein, PMN = polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Gerlofs-Nijland, B. G. H. Bokkers, H. Sachse, J. J. E. Reijnders, M. Gustafsson, A. J. F. Boere, P. F. H. Fokkens, D. L. A. C. Leseman, K. Augsburg, and F. R. Cassee (2019) Inhalation toxicity profiles of particulate matter: a comparison between brake wear with other sources of emission, Inhalation Toxicology, 31:3, 89–98, 10.1080/08958378.2019.1606365 by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis.