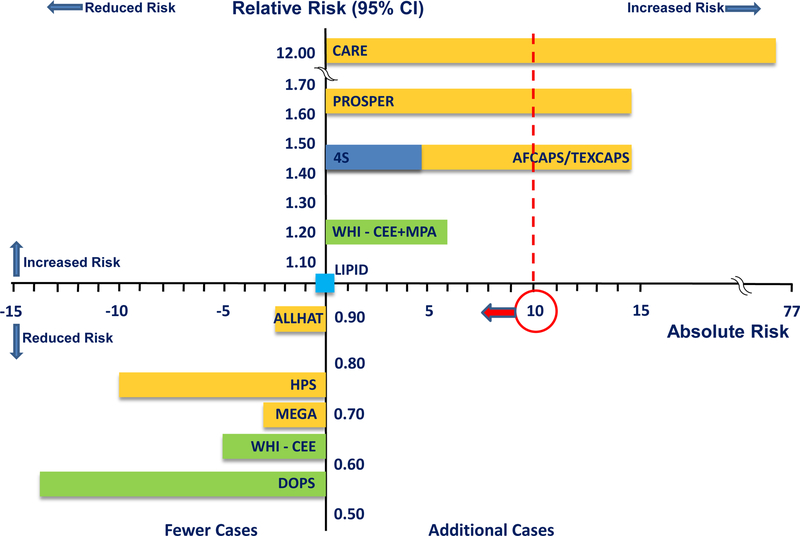
Figure 17.
Comparison of breast cancer incidence from hormone replacement therapy in women <60 years of age when randomized and statin therapy randomized trials. On relative and absolute risk scales, breast cancer incidence from hormone replacement therapy trials (14 fewer to 6 additional breast cancer cases/10,000 women/year of hormone replacement therapy) is similar or less than statin therapy trials (10 fewer to 77 additional breast cancer cases/10,000 women/year of statin therapy). Whereas incidence of breast cancer from hormone replacement therapy is rare, breast cancer incidence from statin therapy exceeds the rare threshold in certain statin therapy trials. Absolute risk of 10 cases/10,000 women is delineated to show relation of breast cancer incidence to the category of rare frequency of events (Table 4). CARE = Cholesterol and Recurrent Events [Pravastatin] (52); PROSPER = Prospective Study of Pravastatin in the Elderly at Risk [Pravastatin] (53); 4S = Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study [Simvastatin] (54); AFCAPS/TEXCAPS = Air Force/Texas Coronary Atherosclerosis Prevention Study [Lovastatin] (55); WHI-CEE+MPA = Women’s Health Initiative Conjugated Equine Estrogen plus Medroxyprogesterone Acetate trial (31); LIPID = Long-Term Intervention with Pravastatin in Ischemic Disease [Pravastatin] (56); ALLHAT = Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial [Pravastatin] (57); HPS = Heart Protection Study [Simvastatin] (58); MEGA = Management of Elevated Cholesterol in the Primary Prevention Group of Adult Japanese [Pravastatin] (35); WHI-CEE = Women’s Health Initiative Conjugated Equine Estrogen trial (31); DOPS = Danish Osteoporosis Study (22); CI = confidence interval