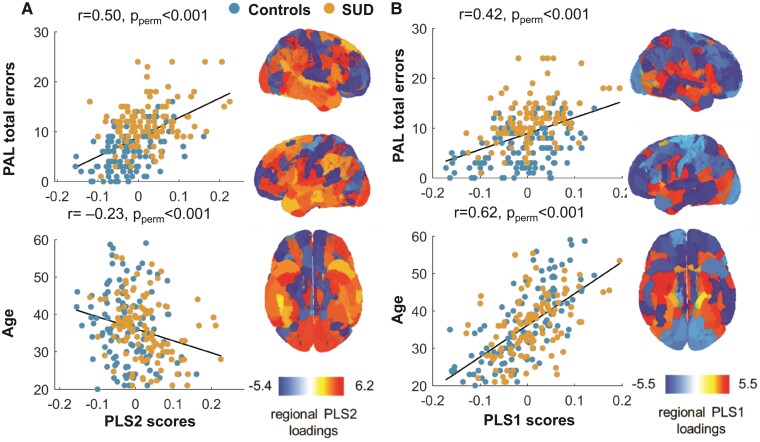
Figure 4.
Brain-cognition association between MS and paired associates learning. Relationship between PAL, age, MS and stimulant drug use. The first two components of the PLS regression jointly explained 43.4% of variance in PAL total errors and age, and 4.35% of variance in regional MS in all 360 regions of interest. PLS2 explained a significant amount of variance in PAL performance and age (15.5%, Pperm = 0.02) but showed a strong positive association with PAL errors and a weak negative association with age (A). PLS1 also explained a significant amount of variance in PAL performance and age (27.9%, Pperm = 0.02) and was positively associated with both of these variables (B). The pattern of regional MS loadings on PLS1 (r = 0.385, Pperm = 0.37) and PLS2 (r = 0.165, Pperm = 0.44) was distinct from the pattern of the control versus stimulant use disorder group difference t-statistics (see Fig. 1C).