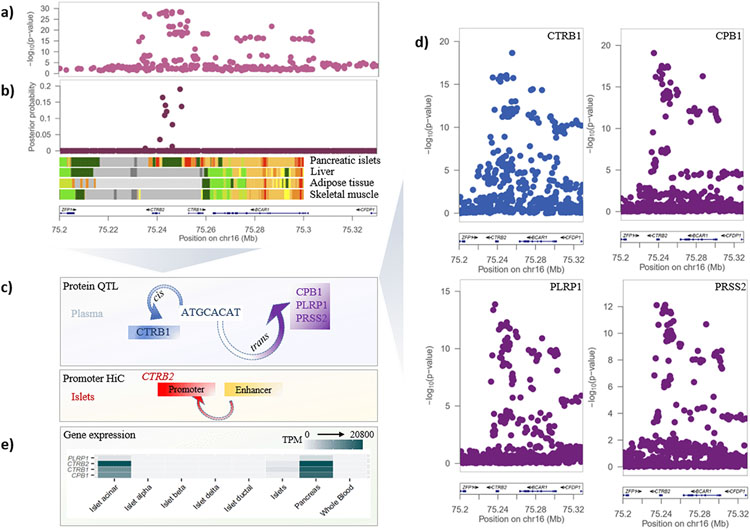
Figure 2 ∣. T2D association signal at the BCAR1 locus colocalizes with multiple circulating plasma pQTLs.
a, Signal plot for T2D association from multi-ancestry meta-regression of 180,834 cases and 1,159,055 controls of diverse ancestry. Each point represents an SNV, plotted with their P-value (on a log10 scale) as a function of genomic position (NCBI build 37). Gene annotations are taken from the University of California Santa Cruz genome browser. Recombination rates are estimated from the Phase II HapMap. b, Fine-mapping of T2D association signal from multi-ancestry meta-regression. Each point represents an SNV plotted with their posterior probability of driving T2D association as a function of genomic position (NCBI build 37). Chromatin states are presented for four diabetes-relevant tissues: active TSS (red), flanking active TSS (orange red), strong transcription (green), weak transcription (dark green), genic enhancers (green yellow), active enhancer (orange), weak enhancer (yellow), bivalent/poised TSS (Indian red), flanking bivalent TSS/enhancer (dark salmon), repressed polycomb (silver), weak repressed polycomb (Gainsboro), quiescent/low (white). c, Schematic presentation of the single cis- and multiple trans- effects mediated by the BCAR1 locus on plasma proteins and the islet chromatin loop between islet enhancer and promoter elements near CTRB2. d, Signal plots for four circulating plasma proteins that colocalize with the T2D association in 3,301 European ancestry participants from the INTERVAL study. Each point represents an SNV, plotted with their P-value (on a log10 scale) as a function of genomic position (NCBI build 37). e, Expression of genes (transcripts per million, TPM) encoding colocalized proteins in islets, pancreas and whole blood.