Extended Data Fig. 5. Putative biochemical pathway from 7 to oxidized Xenia diterpenoids.
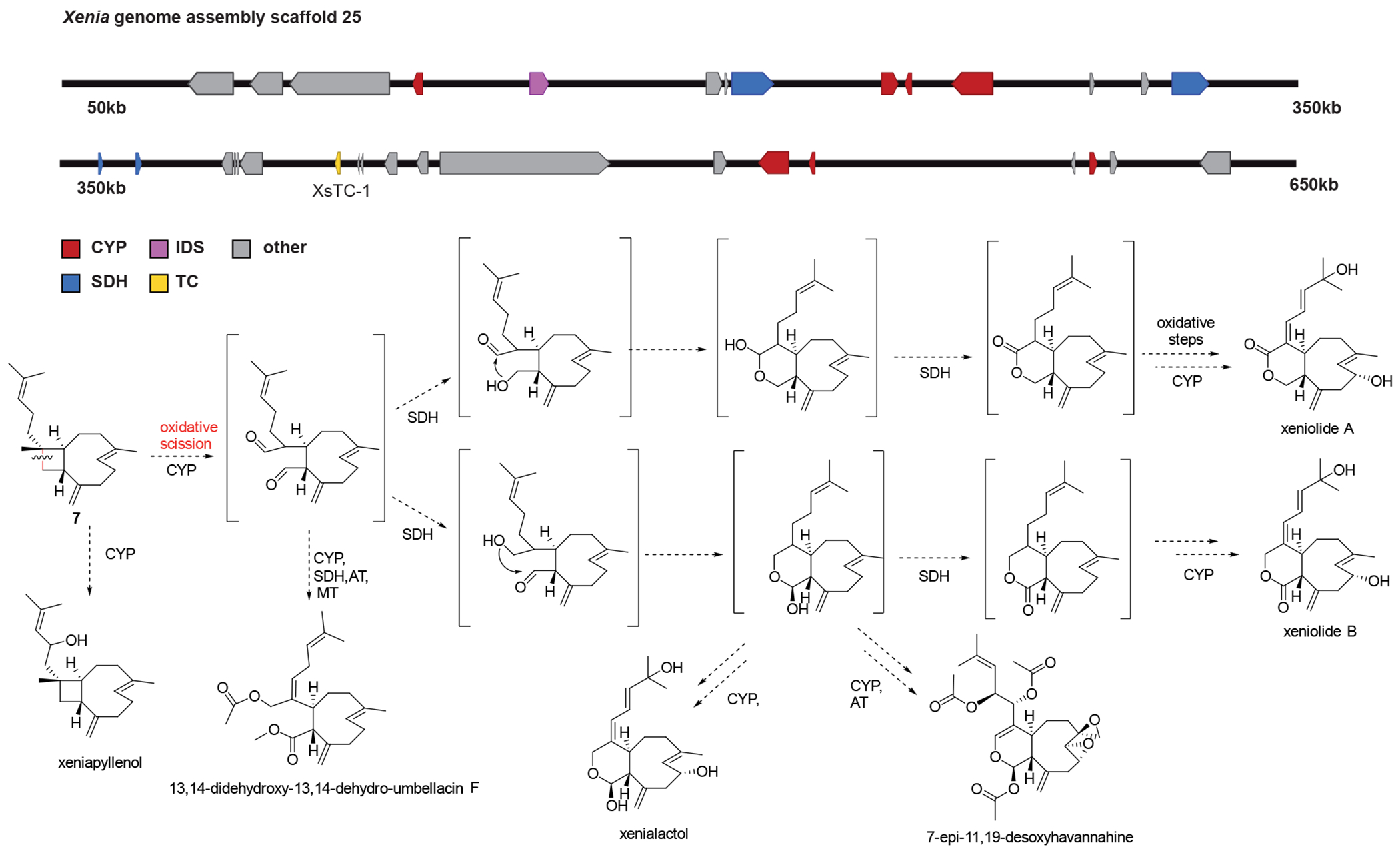
A: Putative terpenoid cluster including Cytochrome P450 genes and short chain dehydrogenase genes additionally to the characterized terpene cyclase XsTC-1, which produces 7. B: Putative overview how different compounds isolated from Xenia spp. and closely related corals could be explained from 7 using CYP and SHD chemistry. The oxidative cleavage of the cyclobutene ring in 7 has been proposed in the literature28. The end points of these putative biochemical pathways all represent isolated molecules from different Xenia spp.8 and could all result from CYP and SDH chemistry following the outlined scheme. Acylations and methylations are also observed in some compounds but could be the result of non-clustered specific or promiscuous enzymatic activity.
CYP = cytochrome P450 monooxygenase, IDS = isoprenyl diphosphate synthase, SDH = short-chain dehydrogenase, TC = terpene cyclase, MT = methyl transferase, AT = acyl transferase.
