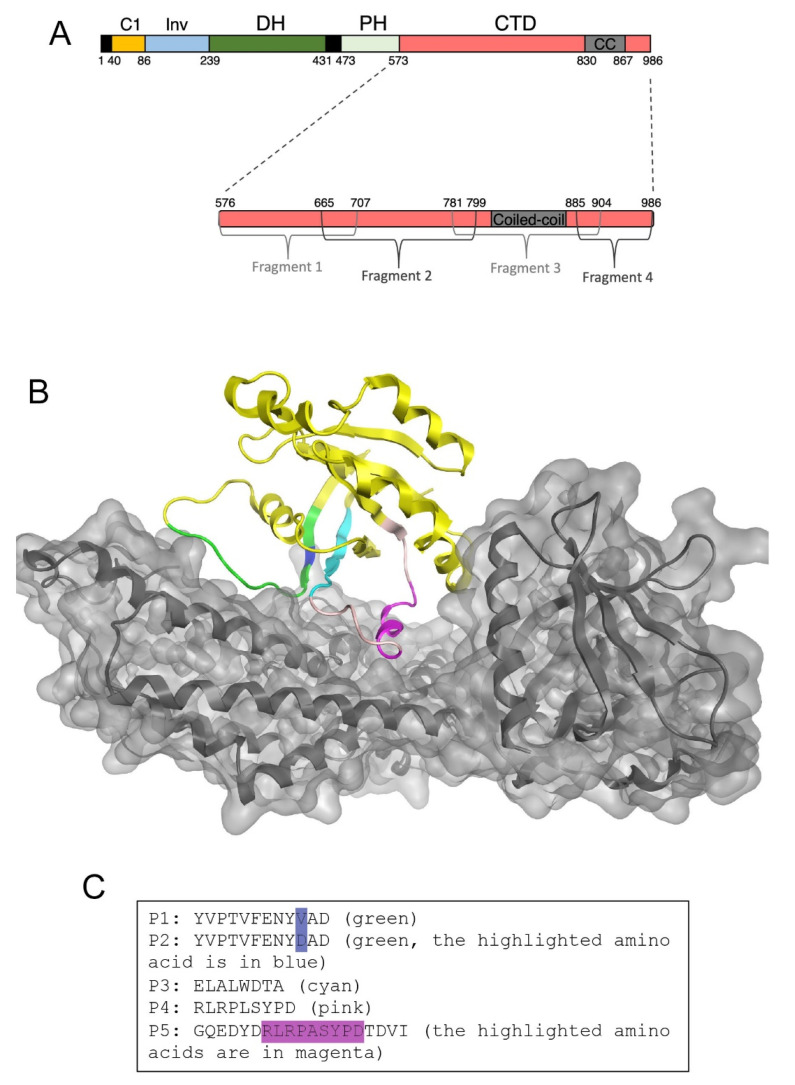
Figure 1.
Design of GEF-H1 inhibitors. (A) Domain structure of GEF-H1. Indicated are the C1 domain, an intervening (Inv) domain linking the C1 to the Dbl homology domain (DH), the Pleckstrin homology domain (PH), and the C-terminal auto-inhibitory domain (CTD). Removal of the C1 domain and CTD domain leads to a constitutive active mutant (GEF-H1-CA; consisting of Inv, DH, and PH domain) as the C1 domain mediates sequestration of GEF-H1 to microtubules and the CTD contains an auto-inhibitory activity. The inhibitory domain was divided into four fragments that were tested for GEF-H1 inhibition to localize the inhibitory activity in GEF-H1′s CTD. (B) Structural modeling of the DH/PH module of GEF-H1 with RhoA. The sequences corresponding to the DH/PH module of GEF-H1 were fitted into the existing crystal structures of RhoA-bound to other Dbl family guanine nucleotide exchange factors (1XCG). The secondary structure of RhoA is represented in yellow ribbons. P1 and P2 peptides are in green; P3 in cyan, and P4 and P5 are in pink/cyan. GEF-H1 is in grey. The resulting interaction surface of GEF-H1 with RhoA was used to select sequences of RhoA likely to be important for binding of RhoA to GEF-H1. (C) The sequences of the peptides inhibitors derived from the structural model that were synthesized for experimental validation.