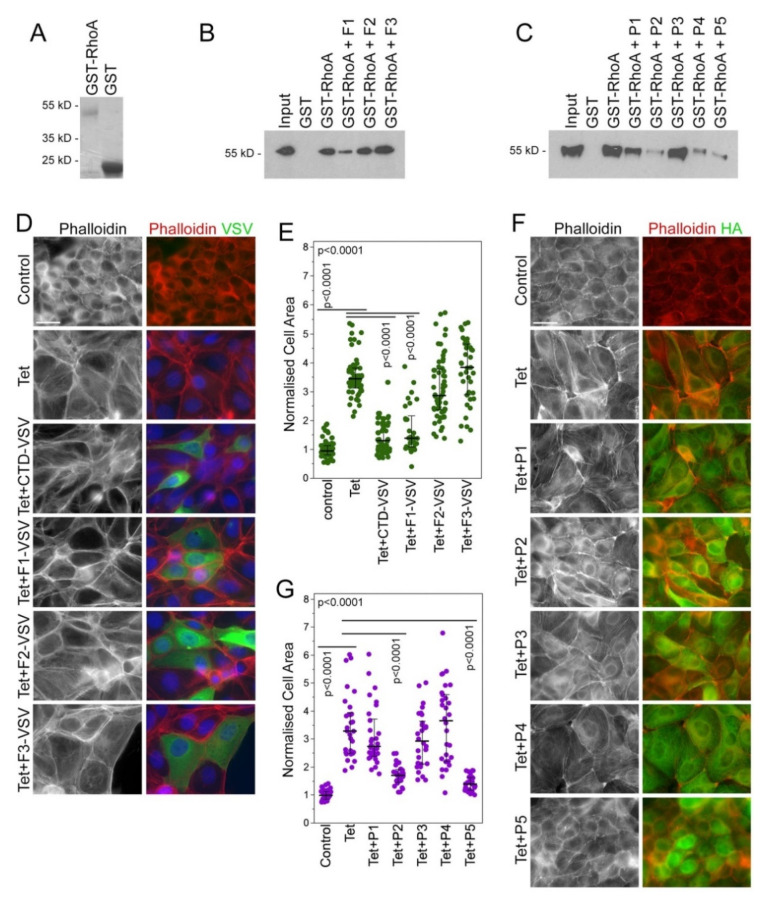
Figure 2.
Selection of GEF-H1 inhibitors that inhibit RhoA binding and GEF-H1 overexpression phenotypes. (A–C) Recombinant fusion proteins of GST and RhoA were used for pulldown of constitutively active GEF-H1 from cell extracts. Candidate fragments and peptide inhibitors were added to the pulldown. Recombinant fragments from the CTD of GEF-H1 (B) or peptides (C) were added. Note, F1 and P2, P4 and P5 peptide inhibitors block the interaction between RhoA and active GEF-H1. (D–G) A stable cell line for tetracycline (Tet)-inducible expression of HA-tagged GEF-H1 was transiently transfected with plasmids encoding VSV-tagged CTD fragments of GEF-H1 (D) or candidate peptide inhibitors (F). The cells were then fixed and stained for either F-actin with fluorescently labeled phalloidin and the VSV-epitope to detect cells expressing the VSV-tagged CTD fragments (D) or fluorescently labeled phalloidin and the HA-epitope to reveal expression of HA-tagged GEF-H1 (F). Cell areas were then quantified as a measure of cell spreading, which increases in response to GEF-H1 overexpression (E,G). The quantifications show values for cell sizes measured over 2 (E) or 3 (G) experiments. P-values were calculated with Wilcoxon and Mann-Whitney tests. Scale bars, 20 μm.