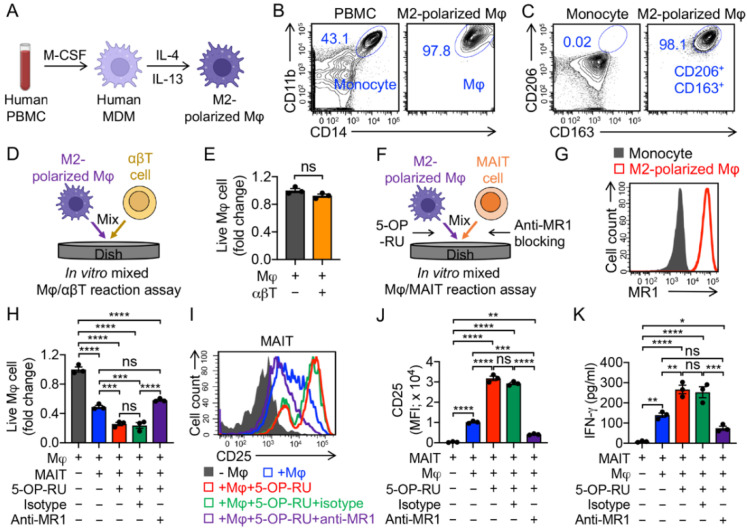
Figure 3.
In vitro targeting of immunosuppressive macrophages by PBMC-derived MAIT cells. (A–C) In vitro generation and polarization of human monocyte-derived M2 macrophages. (A) Experimental design. M-CSF, macrophage colony-stimulating factor; MDM, monocyte-derived macrophage; Mφ, macrophage. (B) FACS detection of CD11b and CD14 on M2-polarized macrophages. Healthy donor PBMCs were included as a staining control. (C) FACS detection of M2 macrophage markers (i.e., CD163 and CD206) on M2-polarized macrophages. Monocytes were included as a control. (D,E) Studying macrophage targeting by αβ T cells using an in vitro mixed macrophage/αβ T cell (Mφ/αβT) reaction assay. (D) Experimental design. (E) FACS analysis of live macrophages 24 h after co-culturing with αβ T cells. Live cells were identified as e506−CD14+CD11b+ (n = 3). (F–K) Studying macrophage targeting by MAIT cells using an in vitro mixed macrophage/MAIT cell (Mφ/MAIT) reaction assay; 5-OP-RU was added to activate MAIT cells. (F) Experimental design. (G) FACS detection of MR1 on monocytes and M2-polarized macrophages. (H) FACS analysis of live macrophages 24 h after co-culturing with MAIT cells. (I) FACS detection of CD25 expression on MAIT cells. (J) Quantification of I (n = 3). (K) ELISA analysis of IFN-γ secretion by MAIT cells in the supernatants of various mixed cell cultures (n = 3). Representative of three experiments. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. ns, not significant, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001, by Student’s t test (E), or by one-way ANOVA (H,J,K).