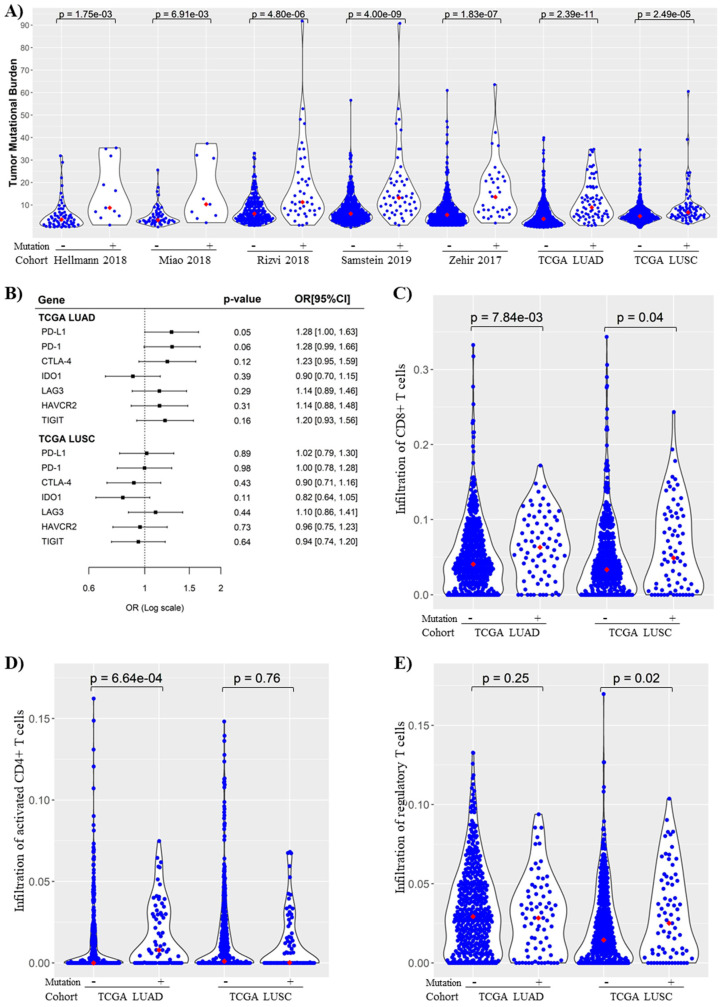
Figure 6.
KMT2C/BCOR/KDM5C mutations were associated with increased tumor mutational burden (TMB) and immunogenicity in NSCLC. (A) Correlation between KMT2C/BCOR/KDM5C mutations and TMB levels in NSCLC. Seven NSCLC cohorts were analyzed as indicated. Each dot represents one sample and red dots represent median TMB values. (B) Logistic regression analysis of the correlation of KMT2C/BCOR/KDM5C mutations with expression of immune checkpoint-related genes in TCGA LUAD and LISC cohorts (mutant as event and wild-type as non-event). Univariate logistic regression was used to compute the OR (per one-SD) with the increase of gene expression (used as a continuous variable). (C–E) Correlation of KMT2C/BCOR/KDM5C mutations with infiltration of CD8+ T cells (C), activated CD4+ T cells (D) and Regulatory T cells (E) in TCGA LUAD and LISC cohorts. Each dot represents one sample and red dots represent median values of cell infiltration level. Wilcoxon signed rank test was used to compare the difference in KMT2C/BCOR/KDM5C mutant and wild-type groups.