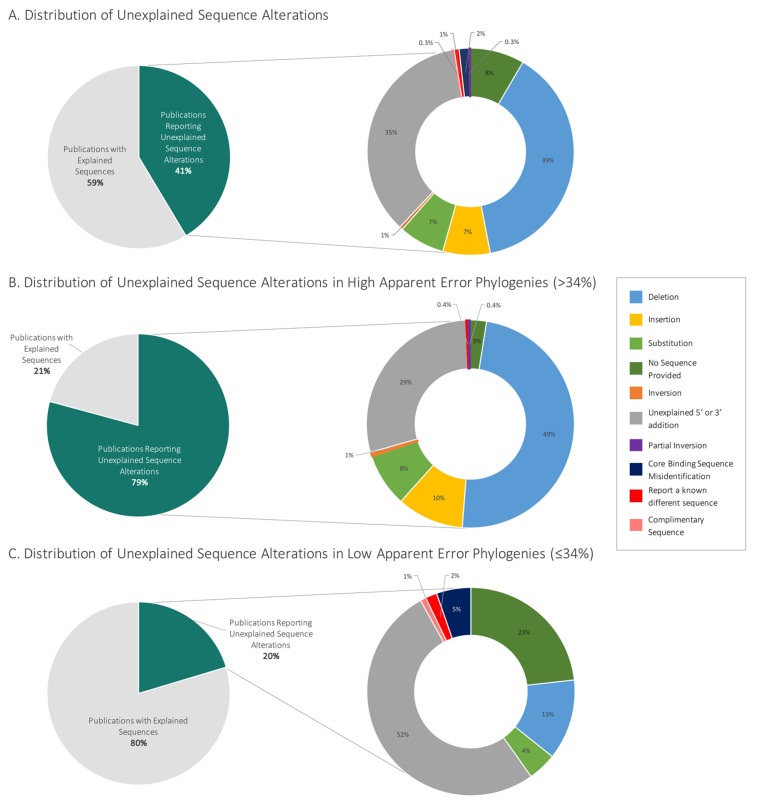
Figure 2.
Distribution of field-wide unexplained aptamer sequence alterations. (A) The breakdown of all publications examined (n = 780 publications, 23 phylogenies grouped by 11 root aptamer publications). (B) The distributions of phylogenies that contained greater than the median of 34% unexplained internal sequence alteration (five phylogenies: Cox lysozyme, lysozyme (DNA aptamer), ATP, PDGF BB, cocaine). (C) The distribution of phylogenies that contained less than or equal to the median of 34% internal mutations (six phylogenies: nucleolin, IgE, theophylline, VEGF, ochratoxin A, thrombin). The percentage of unexplained sequence alterations within each phylogeny can be found in Table S2.