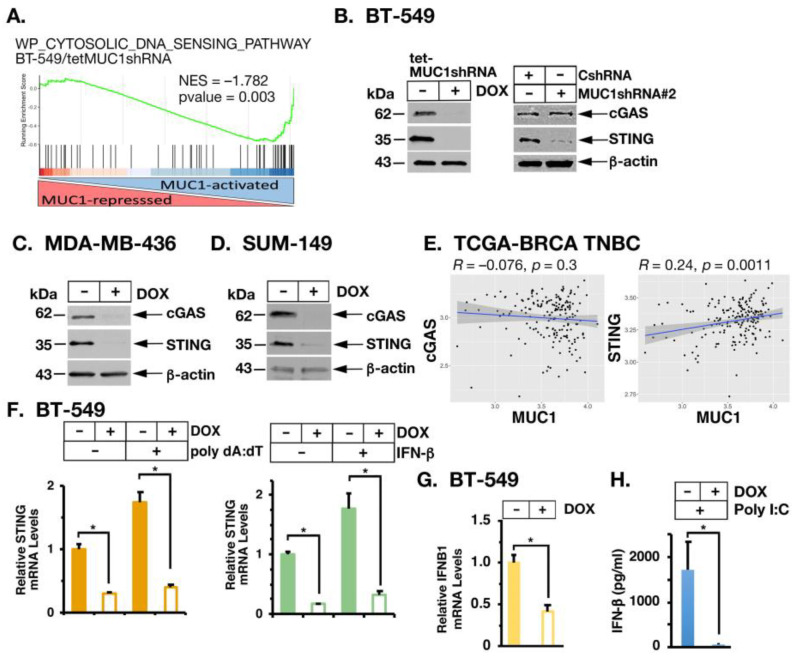
Figure 3.
MUC1-C induces cGAS and STING expression. (A) Candidate enrichment plot of BT-549 RNA-seq data for the WP CYTOSOLIC DNA SENSING PATHWAY gene signature. (B) Lysates from (i) BT-549/tet-MUC1shRNA cells treated with vehicle or DOX for 7 days (left) and (ii) BT-549/CshRNA and BT-549/MUC1shRNA#2 cells (right) were immunoblotted with antibodies against the indicated proteins. (C,D) Lysates from MDA-MB-436/tet-MUC1shRNA (C) and SUM149/tet-MUC1shRNA (D) cells treated with vehicle or DOX for 7 days were immunoblotted with antibodies against the indicated proteins. (E) Scatter plots showing correlations of MUC1 with cGAS and STING in TNBCs from the TCGA-BRCA cohort. (F) BT-549/tet-MUC1shRNA cells treated with vehicle or DOX for 7 days and transfected with poly dA:dT for 12 h (left) or stimulated with IFN-β for 24 h (right) were analyzed for STING mRNA levels by qRT-PCR. (G) BT-549/tet-MUC1shRNA cells treated with vehicle or DOX for 7 days were analyzed for IFNB1 mRNA levels by qRT-PCR. The results (meanSD of 4 determinations) are expressed as relative mRNA levels compared to that obtained for vehicle-treated cells (assigned a value of 1). (H) BT-549/tet-MUC1shRNA cells were treated with vehicle or DOX for 7 days and then transfected with poly I:C for 12 h. Supernatants were analyzed for IFN-β levels by ELISA. The results (mean ± SD of 3 determinations) are expressed as IFN-β pg/mL. The asterisk (*) denotes a p-value < 0.05. Uncropped Western Blots can be found at supplemental original images.