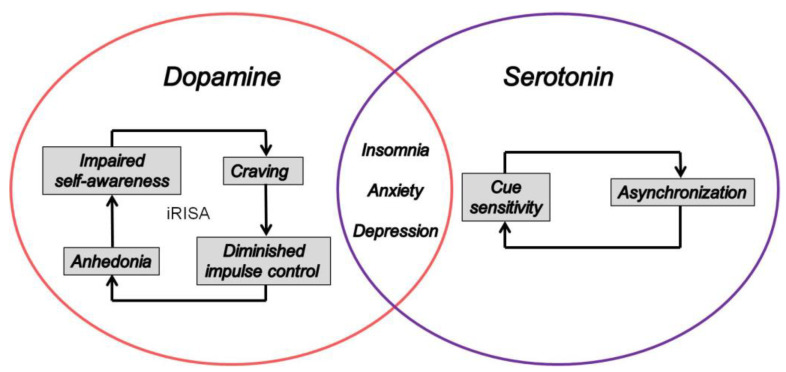
Figure 1.
The iRISA syndrome [76] in addiction is centrally controlled by dopamine in the brain, while asynchronization, presumed to be linked to cue sensitivity in digital addiction [50,51,52,53,54], is centrally controlled by serotonin. A deficit in both neurotransmitters is identified as a brain correlate of insomnia, anxiety, and depression.