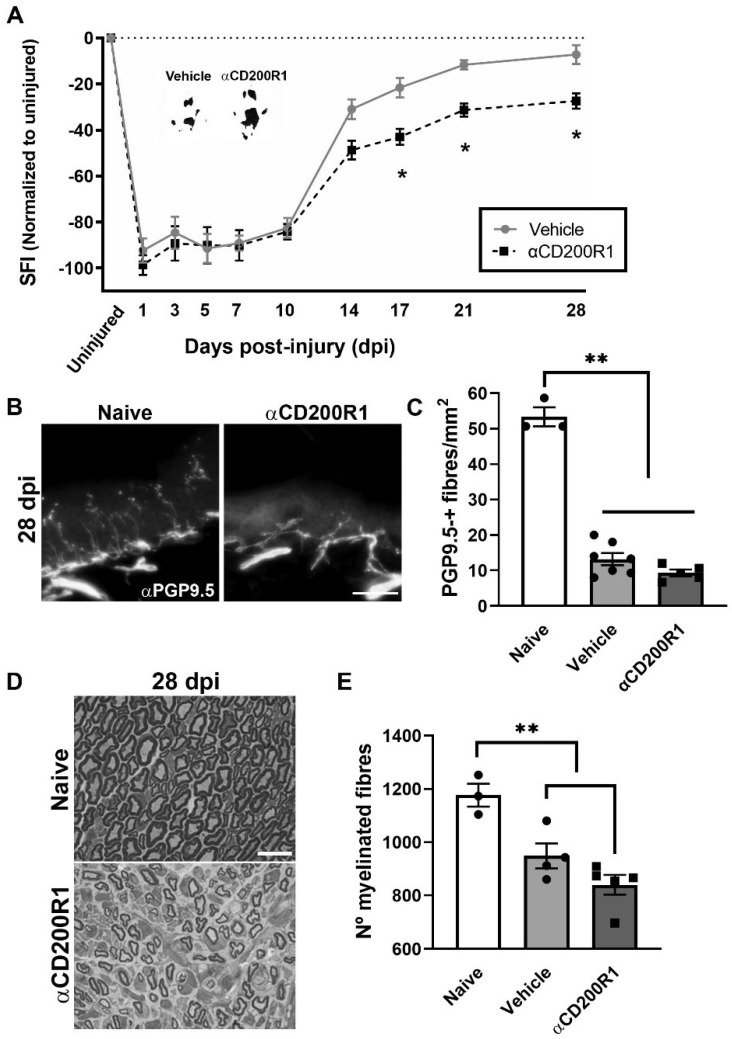
Figure 3.
Blockade of CD200R1 impairs functional recovery after crush injury. The Sciatic Functional Index (SFI) walking track analysis reveals an impairment in the functional recovery from 17 dpi until the last point studied (28 dpi) (A) (Two-way ANOVA, treatment p = 0.002, interaction p = 0.03, Bonferroni’s post-hoc test * p ≤ 0.05; n = 9 vehicle n = 8 αCD200R1). Insert shows representative footprints obtained from the vehicle group and the αCD200R1 treated group at 28 dpi. Representative micrographs of plantar skin immunolabeled against PGP9.5 shows the skin innervation in naive and injured αCD200R1 treated mice. Scale bar: 100 µm (B). Quantification of the number of intraepidermal nerve fibers at 28 dpi shows a dramatic reduction in the skin innervation after injury in both injured groups in comparison with the naive group (C) (One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test; ** p ≤ 0.0001 compared with naive group). Representative micrograph of transverse sections of the tibial nerve at the ankle level at 28 dpi in a naive and injured mouse treated with αCD200R1. Scale bar: 10 µm (D). Quantification of the semithin samples show a reduction in the number of myelinated fibers in both injured groups in comparison to naive (E) (One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test; ** p ≤ 0.001 compared with naive group).