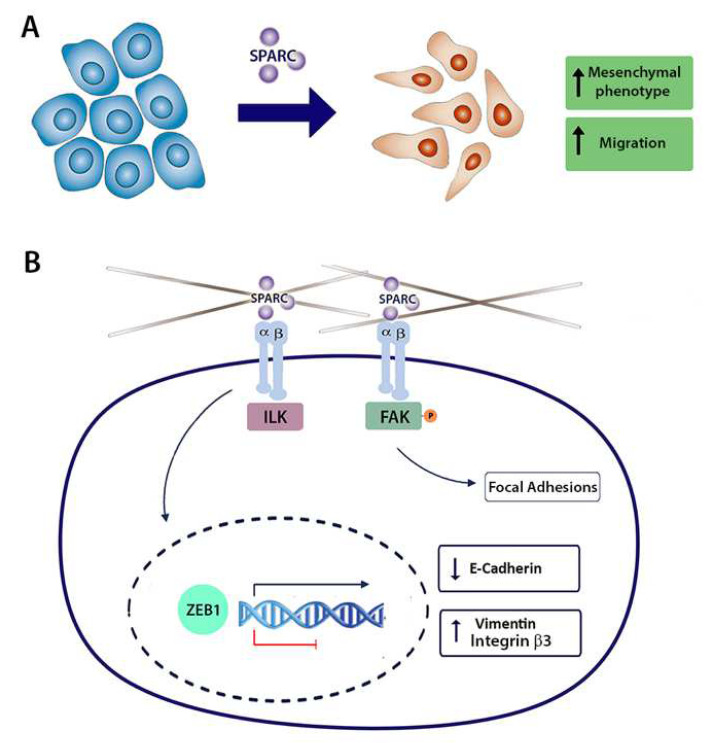
Figure 6.
Proposed model for the effect of SPARC on E-cadherin expression and migration mediated by integrin αvβ3 and the transcription factor ZEB1 in prostate cancer cells. (A) SPARC induces functional changes associated with the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT): increased mesenchymal phenotype and enhanced motility. (B) Because SPARC requires the activity of integrin αvβ3 to induce E-cadherin downregulation and cell migration, SPARC effect could be a result of the direct or indirect association of SPARC and the integrin αvβ3. Through integrin αvβ3, SPARC could activate the focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and the integrin-linked kinase (ILK). FAK activation by phosphorylation on Y925 promotes focal adhesion turnover, enhancing motility. On the other hand, through FAK, ILK, or other downstream molecules, SPARC could be promoting the expression of the EMT transcription factor ZEB1. The transcription factor ZEB1 inhibits the expression of E-cadherin and induces the expression of mesenchymal markers such as vimentin.