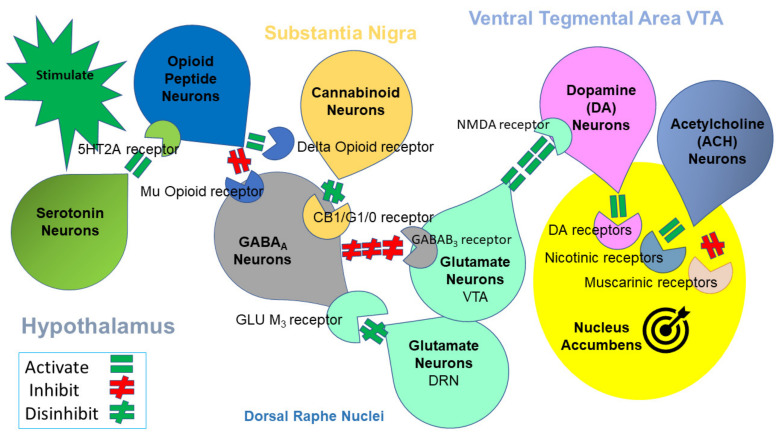
Figure 2.
Mesolimbic Brain Reward Cascade [128]. This cartoon illustrates the interaction of the known major neurotransmitter pathways involved in the Brain Reward Cascade (BRC). In the hypothalamus, environmental stimulation results in the release of serotonin, which in turn, via, for example, 5HT-2a receptors, activates (green equal sign) the subsequent release of opioid peptides from opioid peptide neurons. Then, Substantia Nigra, the opioid peptides move to possibly two different opioid receptors with different effects. One inhibits (red hash sign) through the mu-opioid receptor (possibly via enkephalin) to GABAA neurons. Another stimulates (green equal sign) cannabinoid neurons (the Anandamide and 2-archydonoglcerol, for example) through beta-endorphin-linked delta receptors, which inhibit GABAA neurons. In addition, when activated, cannabinoids, primarily 2-archydonoglerol, can indirectly disinhibit (green hash sign) GABAA neurons through the activation of G1/0 coupled to CB1 receptors. In the Dorsal Raphe Nuclei (DRN), glutamate neurons can then indirectly disinhibit GABAA neurons in the Substantia Nigra through activation of GLU M3 receptors (green hash sign). GABAA neurons, when disinhibited, will, in turn, powerfully (red hash signs) inhibit VTA glutaminergic drive via GABAB 3 receptors. At the Nucleus, Accumbens ACH neurons may stimulate both muscarinic (red hash) and nicotinic (green hash). Finally, glutamate neurons in the VTA will project to dopamine neurons through NMDA receptors (green equal sign) to preferentially release dopamine at the Nucleus Accumbens (NAc), shown as a bullseye, indicating a euphoria, or “wanting” response. The result is dopamine release; low release is (endorphin deficiency), and unhappiness is felt. General (healthy) happiness depends on the dopamine homeostatic tonic set point (with permission) [22]. Notably, various hypotheses have explained the findings that led to the modern known correlates of neurotransmitter interactions within this brain reward circuitry.