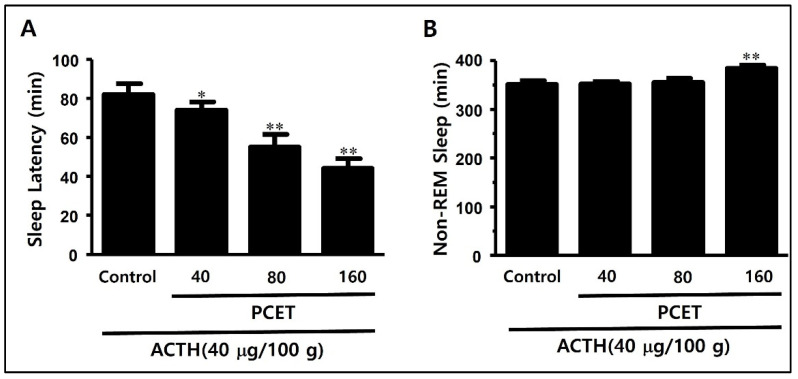
Figure 9.
PCET effect on improving sleep disorders by subcutaneous ACTH injection. The subcutaneous injections of ACTH (400 μg/kg) in SD rats on days 1, 5, and 10, followed by oral gavage of PCET (40, 80, 160 mg/kg), resulted in (A) a significant concentration-dependent decrease in sleep latency, and (B) a significant increase in non-REM sleep time at maximum dosage (160 mg/kg). The data are shown as mean ± standard deviation. Each group consists of three rats. The statistical significance was evaluated based on the p-value, and * p < 0.01 and ** p < 0.001 indicate significant differences from the control.