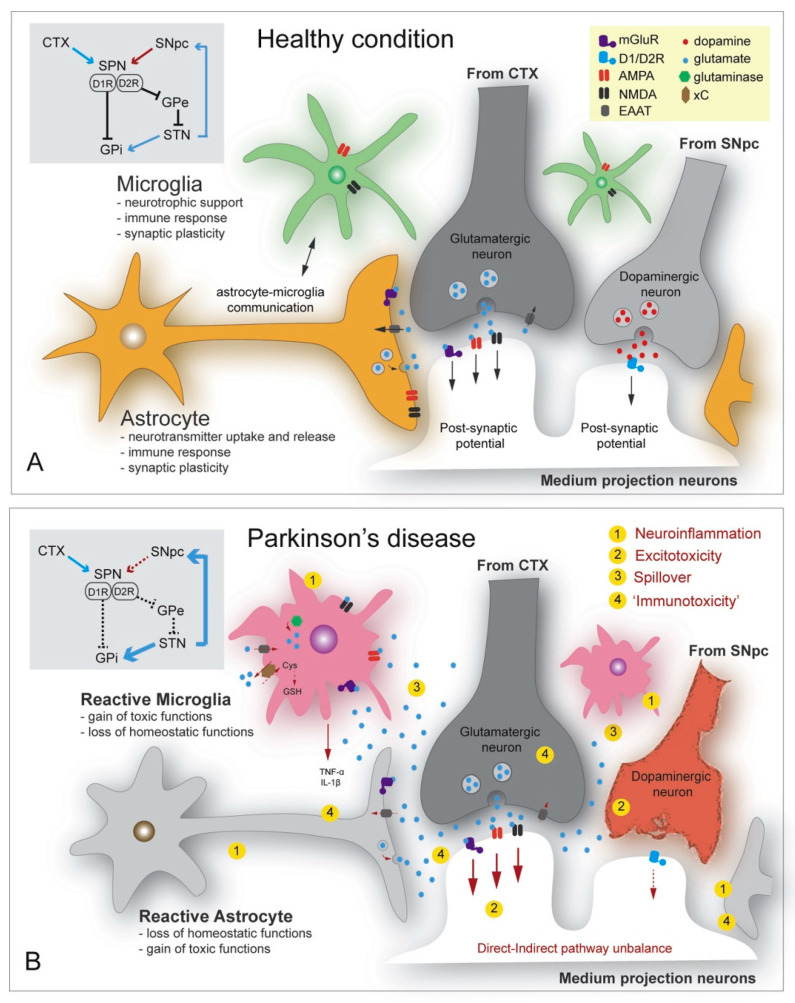
Figure 5.
Glutamate and dopamine-related striatal events—focus on astrocytes and microglia functions in (A) healthy state, (B) Parkinson’s disease (PD) condition. Grey box: fronto-basal circuits involved in the modulation of voluntary movements and impaired connectivity caused by dopamine degeneration in PD. Reprinted from an open-access source [15]. Abbreviations: AMPA—alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid; CTX—cerebral cortex; Cys—cysteine; EEAT—excitatory amino acid transporter; GPe—external segment of the globus pallidus; GPi—internal segment of the globus pallidus; GSH—glutathione; mGluR—metabotropic glutamate receptor; NMDA—N-methyl-D-aspartate; SNpc—substantia nigra pars compacta; SPN—spiny projection neuron; STN—subthalamic nucleus; xC—cysteine–glutamate exchange system.