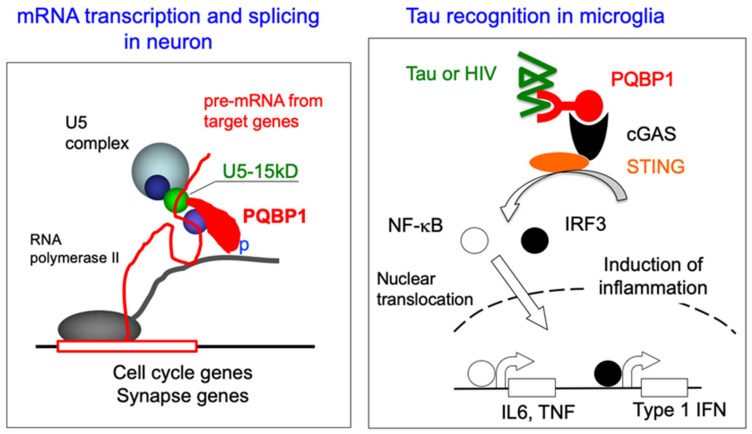
Figure 4.
PQBP1 functions in the nucleus of neurons and the cytoplasm of microglia. (Left) In neurons, PQBP1 functions as an adaptor between transcription and splicing. Immediately after hnRNA (pre-mRNA), splicing complexes assemble for cleavage of intron. PQBP1 binds to the C-terminal tail of RNA polymerase II in a phosphorylation-dependent manner and promotes the splicing of specific types of hnRNAs. PQBP1 is known to directly interact with U5-15kD in U5 spliceosome. (Right) In microglia, PQBP1 is known to play another role as an intracellular receptor for pathogens. PQBP1 recognizes cDNA of HIV to trigger cGAS-STING signaling pathway for inflammation. Recently it is shown that PQBP1 recognizes the Tau protein, which is implicated in Alzheimer’s disease and various Tauopathies in a similar manner than if the Tau were a pathogen. It is yet to be investigated whether PQBP1 triggers cGAS-STING pathway in neurons or whether PQBP1 regulates splicing in microglia.