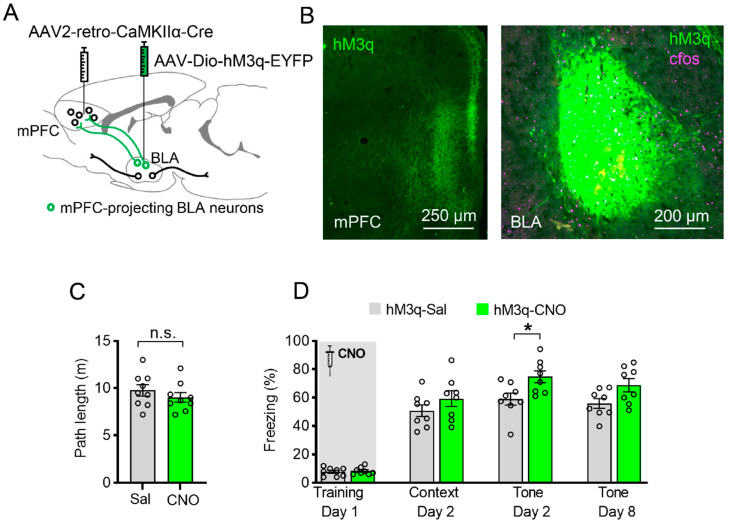
Figure 5.
Specific chemogenetic activation of mPFC-projecting BLA neurons during learning enhances auditorily cued fear memory. (A) Schematic of the experiment: AAV2-retro-CaMKIIα-Cre was injected into the mPFC, and AAV2/9-syn-DIO–hM3q–EYFP was injected into the BLA. (B) Left: hM3q-positive axons (green) of BLA projection neurons are clearly visible in the mPFC. Right: hM3q (green) in BLA neurons projecting to the mPFC with c-Fos staining (pink). (C) Mice expressing hM3q in the mPFC-projecting BLA neurons were injected with either saline or CNO 30 min before FC training. CNO application before training had no significant effect on motor behavior (p = 0.3531, unpaired Student’s t-test, n.s. stands for no significance). (D) CNO application had no significant effect on contextual freezing level on day 2 (p > 0.4811) but promoted auditorily cued fear memory on day 2 (p = 0.0217) (Saline group n = 8, CNO group n = 8, * stands for p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test, main effect of Sal/CNO: F (1, 14) = 6.968, p = 0.0194). All data are presented as mean ± SEM.