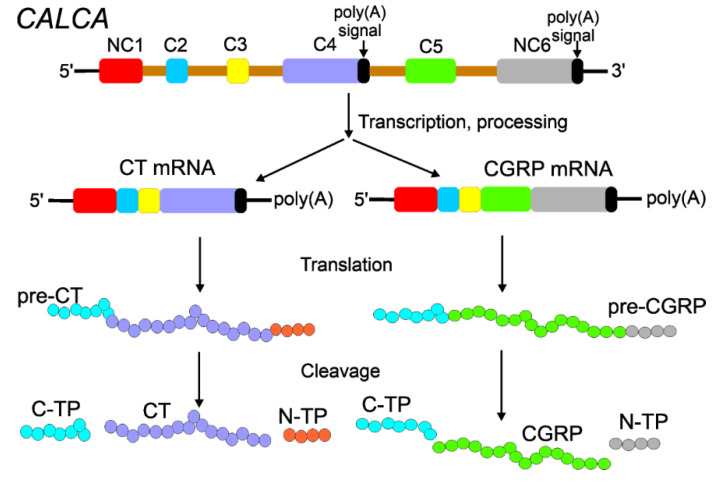
Figure 3.
Alternative processing of the CALCA gene produces calcitonin (CT) and the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP). The CALCA gene has 6 exons separated by 5 introns (gold). Exons 1 and 6 are non-coding exons (NC1, NC6), whereas exons 2–5 are coding exons (C2–C5). Exons 4 and 6 contain signals for polyadenylation (poly(A) signals) that are linked with termination signals in the transcription of the CALCA gene. Therefore, two different CALCA pre-mRNAs having common NC1 + C2 + C3 regions are produced, bearing polyadenylated (poly(A)) tails at their 3′ ends. These two mRNAs are then spliced to produce CT mRNA with four first exons with a poly(A) tail at the 3′ end of exon 4 and CGRP mRNA with three first exons plus exons 5 and 6 with a poly(A) tail at its 3′ end. These two mRNAs are translated to produce CT and CGRP precursors. Post-translational cleavage results in functional CT and CGRP proteins as well as N- and C-terminal peptides (N-TP and C-TP, respectively).