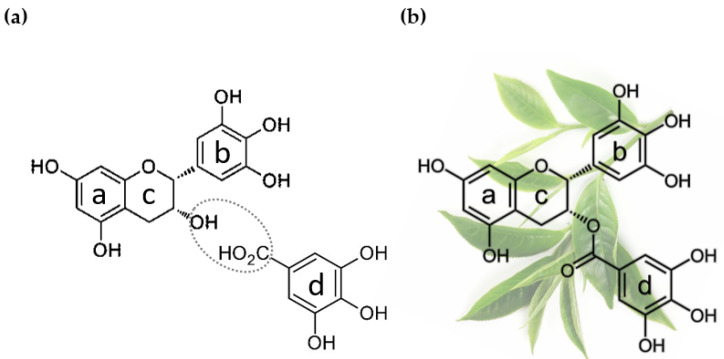
Figure 2.
Origin of epigallocatechin gallate. (a) Chemical structure of epigallocatechin (EGC, above) and gallic acid (below), the two reactants that form epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) via esterification of the circled functional groups. (b) Chemical structure of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), the major constituent of green tea catechins. Background: C. sinensis leaves, from which green tea extracts are produced. The two hydroxylated aromatic rings a and b are connected by a cyclic pyran ring, c; the aromatic ring d is part of the galloyl moiety, the distinctive element of the gallate derivatives of catechins.