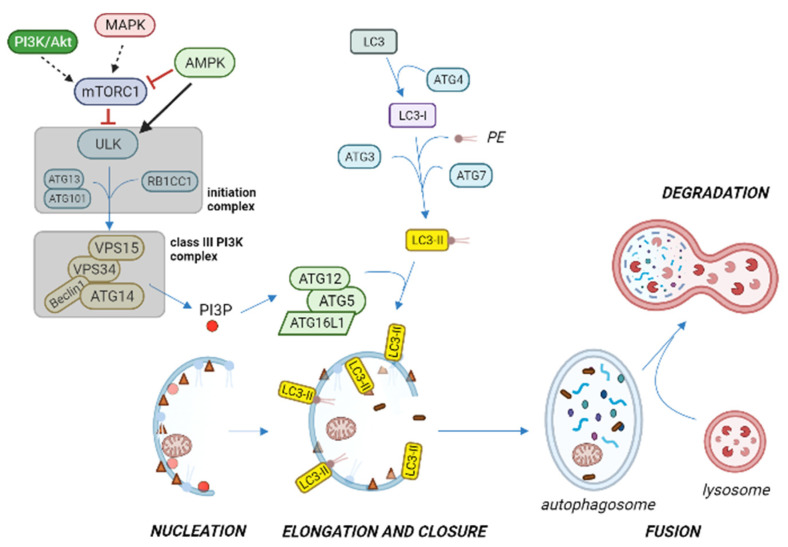
Figure 4.
Overview of autophagy activation pathway under stressful or nutrient limiting conditions. The ULK initiation complex induces phagophore nucleation, and translocates to the endoplasmic reticulum or closely related membranes, where it phosphorylates and activates the class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) complex, thus producing phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PI3P) on the isolation membrane. PI3P recruits specific autophagy effectors that contribute to ATG12-ATG5-ATG16L1 complex formation, which promotes microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3 (LC3) in conjugation with phosphatidyl-ethanolamine (PE), with the participation of ATG proteins. When the isolation membrane elongates and closes to form the autophagosome, lipidated LC3 (LC3-II) is integrated in the autophagosome, thus becoming a common autophagosome marker. As the autophagosome matures, it fuses with the lysosome to produce the autophagolysosome, where the inner membrane of the autophagic vesicle and its content are degraded by lysosomal hydrolases. Reduced signaling from MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways on autophagy initiation is represented with dashed arrows. Black arrow and red blunt arrows represent positive and negative regulation, respectively. Figure created with BioRender.com (accessed on 20 April 2022).