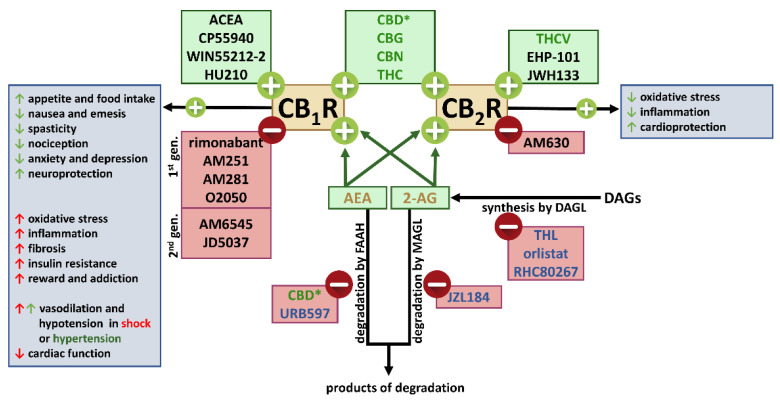
Figure 2.
Simplified diagram of compounds modifying the (endo)cannabinoid system as far as they are considered in this review. The ECS comprises endocannabinoids such as anandamide (AEA), 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), enzymes for their biosynthesis [diacylglycerol lipase (DAGL)] and degradation [fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL)] and cannabinoid receptors (CB1R, CB2R). Green circles with a plus sign describe (partial) agonism at the respective receptor; red circles with a minus sign describe antagonism, inverse agonism, or inhibition at the respective mechanism. Synthetic, plant-derived compounds and endocannabinoids are written in black, green, and brown font, respectively; the blue font is for enzyme inhibitors. Up arrows, increase; down arrows, decrease; green arrows, desired effects; red arrows, undesired effects. 1st gen., first-generation antagonists; 2nd gen., second-generation antagonists; * weak affinity. ACEA, Arachidonyl-2’-chloroethylamide; CBD, cannabidiol; CBG, cannabigerol; CBN, cannabinol; DAGs, diacylglycerols; THC, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol; THCV, tetrahydrocannabivarin; THL, tetrahydrolipstatin.