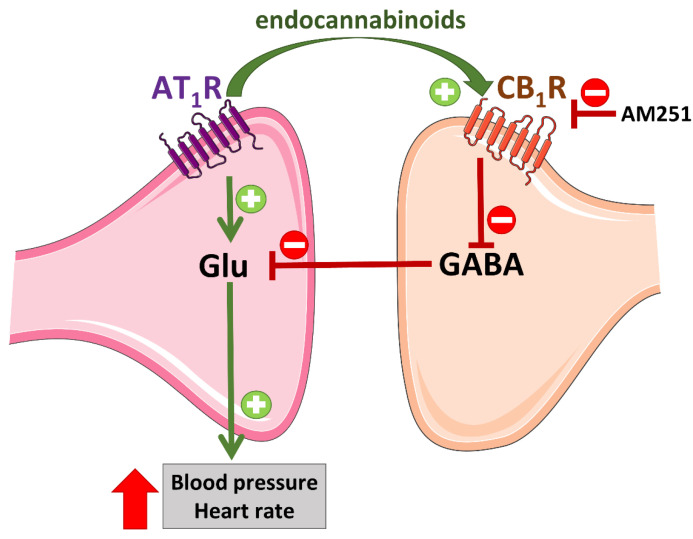
Figure 5.
Potential mechanisms of the cross-talk between AT1 receptors (AT1Rs) and cannabinoid type 1 receptors (CB1Rs) in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. AT1R activation increases blood pressure and heart rate due to a direct and indirectly mediated increase in glutamate (Glu) release. The indirect effect involves an inhibitory γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) interneuron. In detail, AT1R activation increases the release of endocannabinoids (mainly 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol) acting at presynaptic cannabinoid CB1 receptors (CB1Rs), activation of which decreases the inhibitory influence of GABA on sympathoexcitatory glutamatergic neurons. On the other hand, the CB1R antagonist AM251 blocking presynaptic CB1Rs increases the inhibitory influence of GABA on glutamatergic neurons excited by AT1R activation, resulting in a decreased Ang II-induced pressor response. Facilitatory influences are shown by green arrows and plus signs, whereas inhibitory effects are represented by red bars and minus signs.