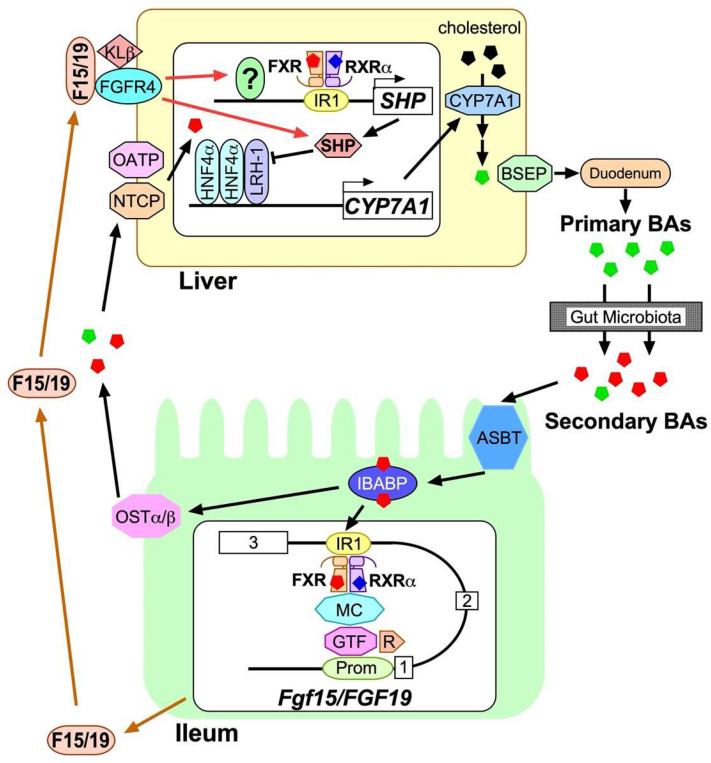
Figure 5.
Regulation of BA synthesis by FXR-FGF15/19 signaling axis. Primary BAs (green pentagons) are synthesized from cholesterol (black pentagons) by a series of enzymatic reactions initiated with CYP7A1 in hepatocytes, and are exported from hepatocytes through BSEP, delivered to the duodenum, and converted to secondary BAs (red pentagons) by gut microbiota when traveling through the intestinal tract to help incorporation of fat-soluble nutrients. The rest of BAs are mostly reabsorbed through ASBT on the apical brush border of enterocytes in the ileum and bind to IBABP. The majority of BAs are then transported to the basolateral membrane to be exported into enterohepatic circulation, whereas a fraction of them is transported to the nucleus to form a complex with FXR and liganded RXRα on IR1 located between exon 2 and 3 of Fgf15/FGF19. The complex is then given access to general transcription factor (GTF) complexes on the promoter region (Prom), mediated by the mediator complex (MC), to initiate RNA polymerization by RNA polymerase II (R). Synthesized FGF15/19 (F15/19) is released into enterohepatic circulation and reaches the FGFR4-Klβ complex to activate intracellular events and induce SHP expression in hepatocytes for subsequent suppression of CYP7A1 expression. Exported BAs into enterohepatic circulation are incorporated into hepatocytes through NTCP or OATP and bind to hepatic FXR-RXRα complex on IR1 of SHP to induce expression. The SHP protein then binds to the HNF4α homodier-LRH-1 complex to suppress CYP7A1 expression.