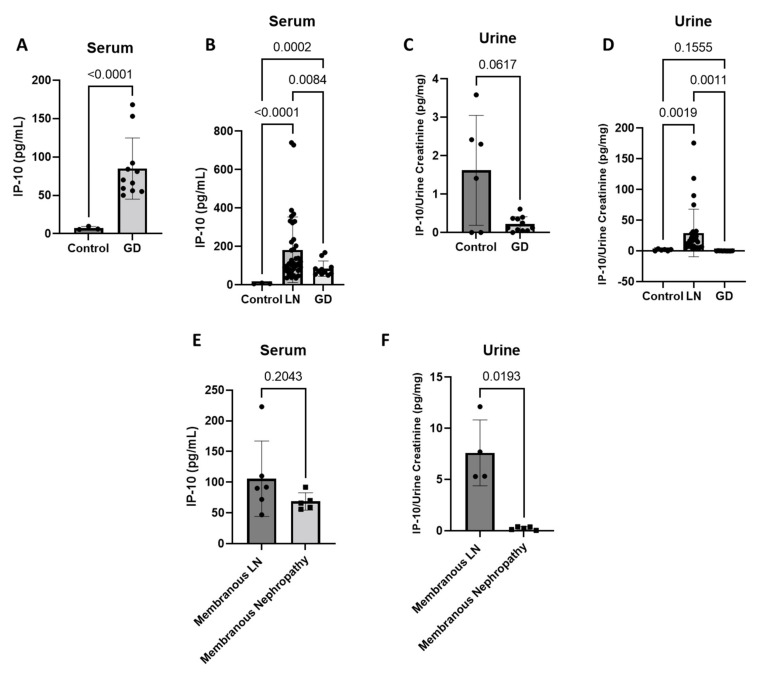
Figure 3.
Urine IP-10 is increased in LN patients versus non-LN glomerular diseases (GD) and Membranous LN compared with primary Membranous Nephropathy. (A) GD serum compared to healthy individuals (control) (n = 3, n = 11; Two-Tailed T-Test with Welch’s correction); and (B) serum IP-10 is significantly increased in LN compared to the GD cohort, and both cohorts’ serum IP-10 levels are significantly increased compared to control (n = 3, n = 36, n = 11; Correction Brown–Forsythe and Welch ANOVA Test, multiple comparisons); (C) IP-10 urine levels are not significantly different in GD compared to control (n = 6, n = 11; Two-Tailed T-Test with Welch’s correction); and (D) in urine, IP-10 is significantly increased in LN compared to GD and control where GD is similar to control levels (n = 6, n = 29, n = 11; correction, Brown-Forsythe and Welch ANOVA Test, multiple comparisons); (E) patients with pure Membranous LN have similar serum IP-10 levels compared to patients with primary Membranous Nephropathy (n = 6, n = 5; Two-Tailed T-Test with Welch’s correction); and (F) patients with pure Membranous LN have increased urine IP-10 levels compared to patients with primary Membranous Nephropathy (n = 4, n = 5; Two-Tailed T-Test with Welch’s correction).