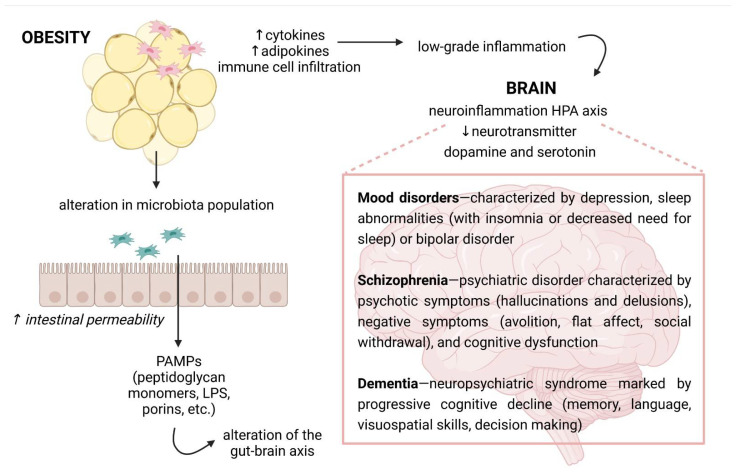
Figure 2.
The possible links between obesity and neurological disorders. Because of a high secretion of cytokines and adipokines by the adipose tissue where immune cells infiltrate, obesity is recognized by chronic low-grade inflammation. Overnutrition is also linked with changes in gut microbiota composition and increased intestinal permeability. Then, it leads the activation of an immune response through microbial or pathogen-associated molecular patterns, e.g., pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS). The inflammatory molecules can reach the circulation and the central nervous system, where they may cause neuroinflammation. In turn, the immune activation in the brain can influence the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis and neurotransmitter signaling, affecting cognition and behavior. Own drawing, based on [116].