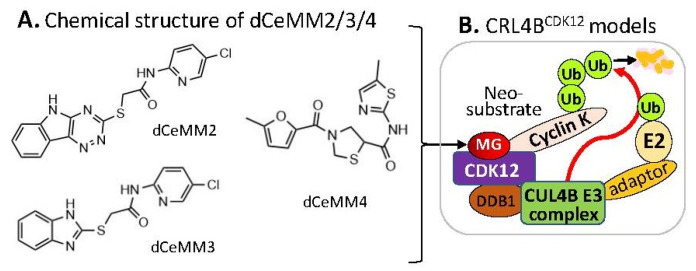
Figure 5.
(A) The chemical structure of dCeMM2, dCeMM3, and dCeMM4 as MG compounds; (B) the substrate receptor-independent E3 ligase protein complex model for ubiquitination of the neosubstrate cyclin K. The MG compounds dCeMM2/3/4 shown in (A) was found through a substrate receptor-independent manner (neither CRBN nor DCAF15 being involved) to glue CDK12-cyclin K directly on DDB1–CUL4B E3 ligase complex to polyubiquitinate cyclin K. Then, the polyubiquitinated cyclin K would be degraded through the ubiquitination proteasome pathway.