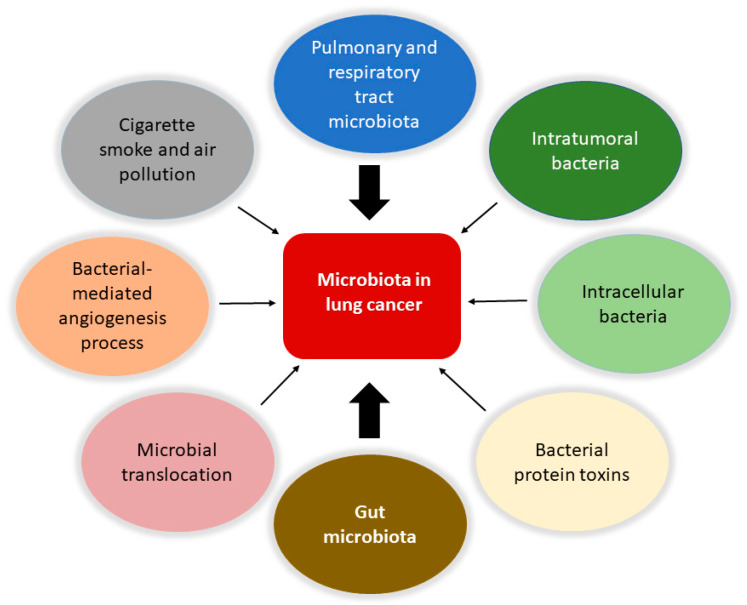
Figure 1.
Involvement of the microbiota in lung cancer. The microbiota is involved in the biology of lung cancer at different levels and through various mechanisms. Protagonists are the bacteria in the upper respiratory and pulmonary tract and those that constitute the tumor microenvironment with intratumoral and intracellular localization. The intestinal microbiota plays a central role in modulating the responses of the immune system and the inflammatory state of the body, together with the bacteria involved in translocation phenomena in the bloodstream. It is also possible that certain bacterial toxins that can activate oncogenic pathways may lead to transformation in the lung. Furthermore, pollution and cigarette smoke are directly responsible for dysbiotic changes in the lung. Finally, the microbiota can affect metastasis processes by increasing the expression of vascular endothelial growth factors and promoting inflammation.