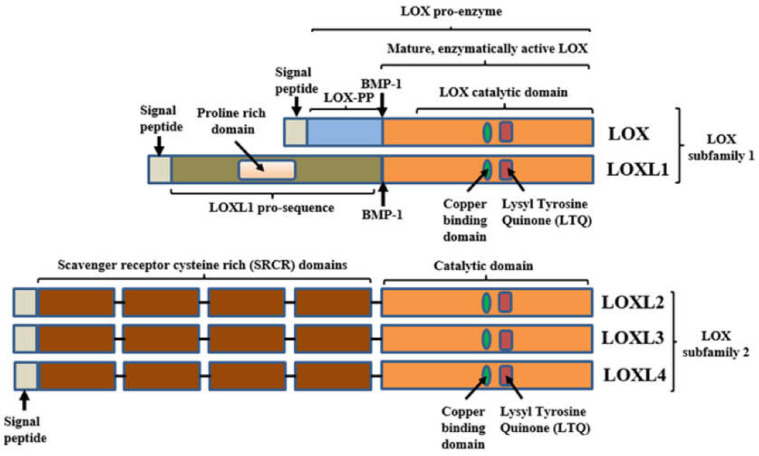
Figure 1.
Structural elements of the lysyl-oxidases: The five lysyl-oxidases can be divided into two sub-families. The first includes LOX and Loxl1. These are synthesize as pro-enzymes that are cleaved by the BMP-1 protease (and in the case of LOX by additional proteases such as ADAMTS2/14) to release the mature active enzyme. The second subfamily includes LOXL2-4 and is characterized by a much less conserved N-terminal that is characterized by the presence of four scavenger receptor cysteine rich (SRCR) domains. The catalytic domain is highly conserved among the different lysyl-oxidases and includes a conserved copper binding domain and a unique lysyl tyrosine quinone (LTQ) element that is essential for the catalytic activity (for a more detailed discussion of the structure and enzyme function of LOX see this review [5]). In the case of LOX cleavage by BMP-1 also releases the N-terminal part, LOX-PP, which functions as a tumor suppressor.