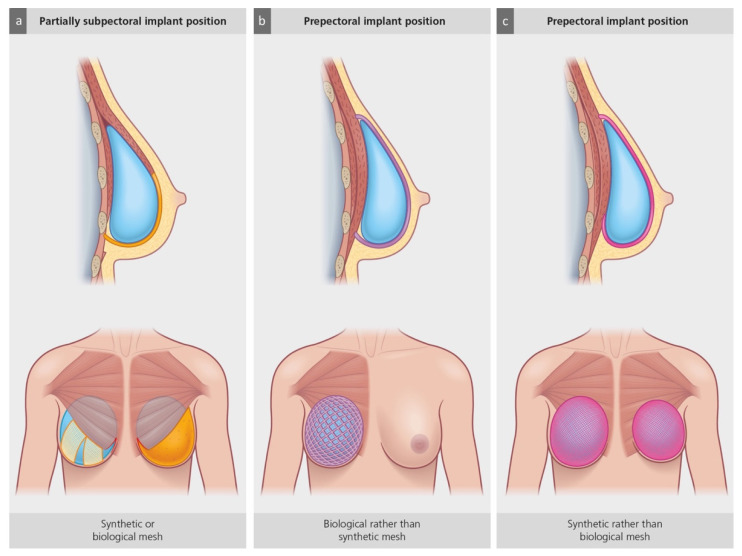
Figure 3.
Schematic drawing of three different clinical situations during implant-based breast reconstruction (BR). (a) Subpectoral placement of an expander or implant requires the partial detachment of the greater pectoral muscle with partial medial disinsertion. Absence of fixation using synthetic mesh strips (right hemithorax) or biologic meshes (acellular dermal matrix; ADM; left hemithorax) will result in cranial muscle retraction. (b) Prepectoral expander or implant placement in patients with thin mastectomy flaps may benefit from thickened adipocutaneous implant coverage, due to ADM or synthetic meshes with tissue-integrative potential. (c) Prepectoral implant placement in patients with a mismatch between the large footprint of the breast after a mastectomy (e.g., breast hypertrophy) or a wide implant pocket in revisional breast surgery (e.g., down-sizing of breast implant volume) and implant size. When using a smaller implant, these patients may benefit from implant positioning and fixation using synthetic, pocket-shaped meshes rather than ADMs.