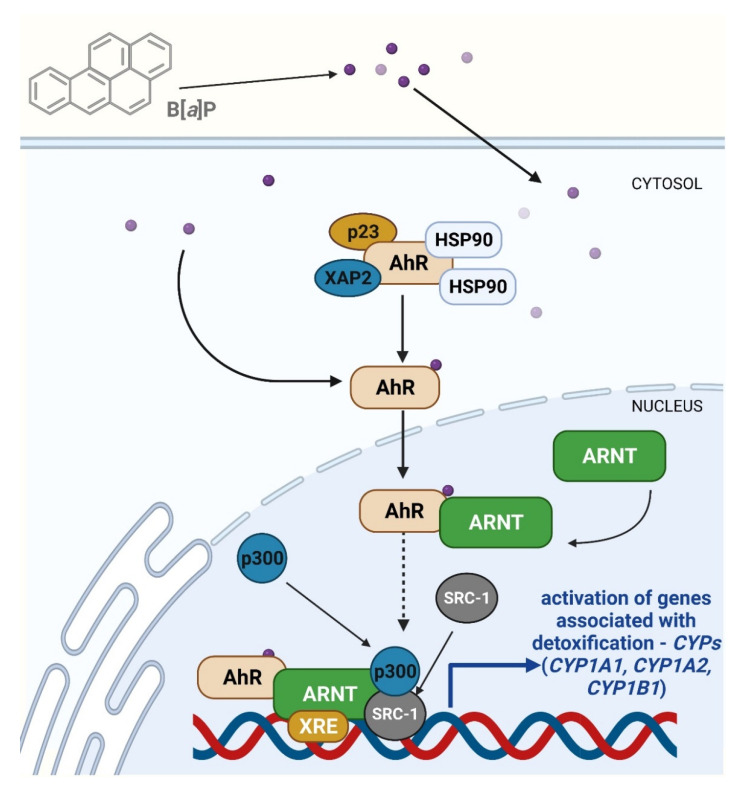
Figure 7.
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a ligand-activated transcription factor located in the cytosol. Inactive AhR occurs as a complex bonded with protein HSP90 (heat shock protein 90), p23 co-chaperone, and protein XAP2 (aryl hydrocarbon receptor-interacting protein, known also as AIP) or arachidonic acid (ARA). Binding AhR with ligand (B[a]P) leads to translocation of the active form of receptor to the nucleus and binds it with AhR receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT). Attachment of specific transcription factors (xenobiotic response element, XRE; histone acetyltransferase p300, steroid receptor coactivator-1, SRC-1) triggers gene machinery leading to activation of detoxification pathways (mainly by cytochrome P450 activation, CYPs). Intensification of ROS production can be correlated with DNA damage, mutation (mainly via PBDE), and carcinogenesis [122]. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 12 April 2022).