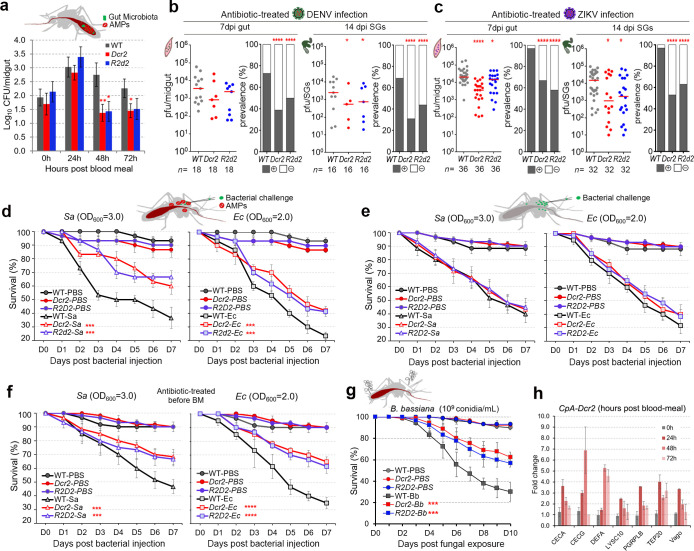
Fig 4. Antimicrobial resistance of siRNA pathway (Dcr2 and R2d2) overexpressing transgenic mosquitoes (Dcr2: CpA-Dcr2, R2d2: CpA-R2d2).
The up-regulation of Dcr2 and R2d2 in the transgenic mosquitoes activates the expression of several AMPs and then modulates the Aedes mosquitoes’ susceptibility to bacterial and fungal infection. (a) The total bacterial loads of the midgut microbiota of female transgenic and WT control mosquitoes at 24, 48, and 72 h PBM (mean ± SEM). A Student t test was used to determine significance. At least 3 biologicals were included with 10 mosquitoes in each replicate. (b and c) DENV2 (b) and ZIKV (c) viral infection intensities and infection prevalence in the aseptic (antibiotic-treated) transgenic and WT mosquitoes at 7 dpi (midguts) and 14 dpi (SGs) showed a similar level of reduction to that in the septic (non-antibiotic-treated) mosquitoes (as shown in Fig 2). At least 3 replicates are included, with each dot representing the viral load and the horizontal line (red) indicating the median value. The Mann–Whitney test was used to assess infection intensity, and the Fisher’s exact test was used to determine the significance of infection prevalence (* P < 0.05, **** P < 0.0001). (d–f) Survival rate of female transgenic mosquitoes after challenge with either gram-positive (S. aureus: 210,000 CFU) or gram-negative (E. coli: 140,000 CFU) bacteria at 7 dpi post a blood meal (d), or without a blood meal (e), or treated with antibiotics for 4 days followed by a blood meal 24 h before bacterial injection (f). (g) Survival rates of female WT, transgenic CpA-Dcr2 and CpA-R2d2 mosquitoes after B. bassiana infection. Prior to assays in (a, d, f, and g), all groups of the female mosquitoes were given a naïve blood meal to up-regulate the expression of the transgenes. The significance of the survival rates was determined by Kaplan–Meier survival analysis from 3 biological replicates with at least approximately 20 to 30 mosquitoes in each replicate (*** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001). (h) qRT-PCR expression profiling of a panel of antimicrobial and immune genes (S3 Table) in the midguts of female CpA-Dcr2 transgenic mosquitoes at 0 h (before a blood meal), 24, 48, and 72 h PBM. The WT midguts were used as the control, and the AeRps17 gene was used as an internal control for normalization. Data underlying this figure can be found in S2 Data. AMP, antimicrobial peptide; CFU, colony-forming unit; DENV2, DENV serotype 2; dpi, days post-infection; PBM, post-blood meal; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time PCR; SG, salivary gland; siRNA, small interfering RNA; WT, wild type; ZIKV, Zika virus.