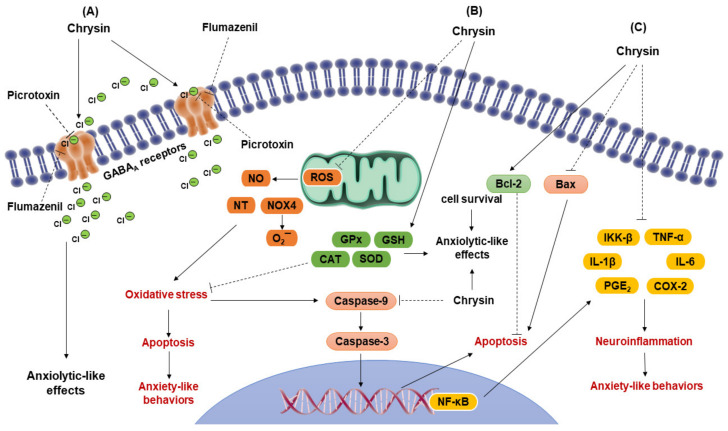
Figure 2.
Mechanism of action of the flavonoid chrysin potentially involved in its anxiolytic-like effects. (A) It has been confirmed that chrysin produces its anxiolytic-like effect through its action on the GABAA/benzodiazepine receptor complex producing configurational changes in the receptor and regulating the opening of the Cl− ion channel [14,15,17,24,35], which may produce inhibitory effects in the GABAergic system associated with its anxiolytic-like effects. These effects can be blocked by specific antagonists of the GABAA receptor, such as picrotoxin, bicuculline, and flumazenil [14]. (B) Probably, antioxidant effects of chrysin could be involved in its anxiolytic-like effects. Chrysin significantly reduces ROS by inhibiting the production of NO, NT, and NOX4 [29]. These effects reduce the oxidative stress and reduces the neuronal damage. Additionally, chrysin reduces the activity of Bax, caspase-9, and caspase-3, while increasing the production of Bcl-2, thereby reducing the damage of DNA and inhibiting apoptotic processes [60,61], which reduces the neuronal death. (C) Additionally, the anti-inflammatory effects of chrysin could contribute to its anxiolytic-like effects, considering that it may reduce the inflammatory response by inhibiting the signaling pathway NF-κB/IKK-β [27,28]. Chrysin may attenuate the expression of NF-κB that participates as transcriptional factors at nuclear level, binding to genes that induce neuro-inflammation process. Chrysin also inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β and IL-6, in addition to suppressing the production of proinflammatory mediators, such as TNF-α, PGE2 and COX-2 [27,28,32]. These effects could reduce neuro-inflammation associated with the anxiety-like behavior. ROS = reactive oxygen species; NO = nitric oxide; NT = nitrotyrosine; NOX4 = NADPH oxidase; O2¯ = superoxide; Green circles = chlorine ions; SOD = superoxide dismutase; GSH = reduced glutathione; CAT = catalase; GPx = glutathione peroxidase; Bcl-2 = anti-apoptotic protein of the subfamily Bcl-2; Bax = pro-apoptotic protein of the subfamily Bax; NF-κB = nuclear factor kappa B; IKK-β = inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B; TNF-α = tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-1β = interleukin-1β; IL-6 = interleukin-6; PGE2 = prostaglandins E2; COX-2 = cycloxygenase-2. (Figure was prepared by the authors).