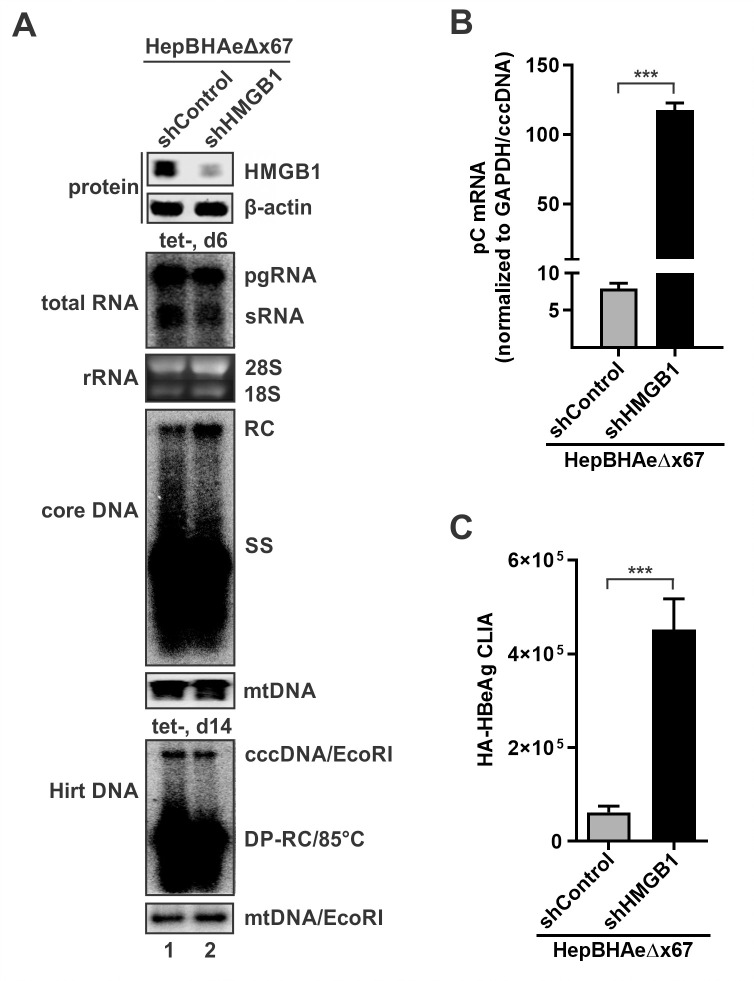
Fig 7. HMGB1 knockdown rescues cccDNA transcriptional activity in the absence of HBx.
(A) Assessment of the HepBHAeΔx67-shControl and HepBHAeΔx67-shHMGB1 cell lines. The knockdown of HMGB1 in HepBHAeΔx67-shHMGB1 cells was validated by Western blot, β-actin served as loading control. After 6-days induction, HBV total RNA was analyzed by Northern blot, cellular 28S and 18S rRNA served as loading control; HBV cytoplasmic core DNA was analyzed by Southern blot, mitochondrial (mt) DNA served as a loading control. After 14-days induction, total cellular Hirt DNA was heat-denatured, followed by EcoRI digestion, and then subjected to Southern blot analyses of HBV deproteinated rcDNA (DP-RC), linearized cccDNA, and mtDNA. (B) The relative levels of HBV cccDNA-dependent pC mRNA in HepBHAeΔx67-shControl and HepBHAeΔx67-shHMGB1 cells were analyzed by qPCR and normalized to cellular GAPDH and cccDNA (mean ± SEM, n = 3). (C) Supernatant HA-HBeAg was detected by CLIA (mean ± SEM, n = 3). ***p<0.001.